It is an indescribable feeling for an athlete to walk into the opening ceremonies of an Olympic Games. I still get chills thinking about that moment for me at the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing, when I represented Canada as a high jumper.
Standing shoulder to shoulder with my teammates, there was a realization we were on the doorstep of something great that was about to begin. The journey to become an Olympic athlete may have been different for each of us, but there is a shared appreciation for how hard it is to get to the Olympic Games.
Sports provide athletes with a unique quality, where they are both the consumer and producer of an event. The success of the Olympic Games and any major sporting event depends on the performances of the athletes. To have a great result, the conditions must be optimal.
From the athletes’ village to competition venues, a positive experience is essential to ensure a great performance. Understanding the needs of the athletes becomes critical to conduct a successful Olympic Games.
Establishing an “athlete-centered” sporting experience has become a ubiquitous pledge of various sports enterprises, including the International Olympic Committee. Even Sport Canada has identified an athlete-centered experience as a factor that provides a leading edge when it comes to high performance.
However, what does it really mean to be athlete-centered?
Athletes Involved In Decision Making
Some researchers have offered a holistic definition where athletes are included in the decision-making process. Some have explained it as encompassing the well-being of an athlete, whereas others have defined it as empowering the athlete and providing a sense of belonging.
AthletesCAN, the official voice of all Canadian national team athletes, has determined “athlete-centered” to be both a concept and a process, underpinning “ the planning, delivery, and procedures of organizing sport.”
For a term recognized as important in the world of sports, it has failed to be consistently and adequately defined. While definitions vary, allowing athletes to have a say in their well-being appears to be a central theme.
In professional sports leagues, player associations ensure the best interests of athletes are served. In amateur sports, there are limited associations by athletes for athletes.
Recently, the International Beach Volleyball Players Association was formed out of protest to changes made by the Fédération Internationale de Volleyball without the input of athletes. As a result of these changes, beach volleyball players experienced diminished prize earnings and canceled tournaments.
Likewise, track-and-field athletes have been working to become unionized for several years. This is a conversation I remember having with other athletes while I was competing as a high jumper at the international level.
Restrictions On Sponsorships
One main issue when it comes to athletes’ rights focuses on sponsorship. Compared to NASCAR, Formula One Racing, or cycling — where athletes can sport numerous sponsor logos on their uniforms — the International Athletic Association Federation, the governing body for track and field, restricts athletes to only one logo no larger than 6 centimeters.
Rule 40, an IOC bylaw that restricts athletes from having their image or performance used for marketing during the Olympic Games, was challenged going into the 2016 Summer Games in Rio de Janeiro.
Athletes argued the IOC reaped the rewards of sponsorship and broadcasting revenue while leaving the athletes — the stars of the show — out in the cold. Because athletes raised so much concern about Rule 40, the IOC has lessened this restriction on athletes, permitting sponsors to apply for Rule 40 waivers that would enable them to continue to market athletes during the Olympic Games.
As we watch the 2018 Winter Games in Pyeongchang, it’s worth evaluating whether athletes are actually the most important part of the Olympics.
Many Controversies Facing IOC
Considering the controversies surrounding the selection of host cities, transgender athletes competing in the Olympic Games, and the IOC’s ruling on Russian athletes competing in Rio during 2016 and this year in Pyeongchang, it is reasonable to question the IOC’s commitment to being athlete-centered.
Even drug testing procedures, which require athletes to report their whereabouts for three months in advance as prescribed by the World Anti-Doping Agency — an organization initiated by the IOC — has come under fire for infringing on athletes’ freedom.
While these concerns are valid, I would still argue the IOC does indeed strive to be athlete-centered.
The IOC’s mission places the interest of athletes at the center of the Olympic movement. Evidence of this is seen with the 12-member elected IOC’s Athletes’ Commission. Its mandate involves representing the views of athletes and advising the IOC Session, the IOC Executive Board, and the IOC president on decisions affecting athletes.
As someone who has served on the Athletes Commission for the Canadian Olympic Committee, I can attest that whenever an athlete speaks up, everyone listens.
Weighing In On Russian Athletes
Amid the Russian doping scandal that has shrouded the last several Olympic Games, athletes have been able to weigh in and influence key decisions. To assist with establishing the pool of clean Russian athletes to be considered for an invitation to compete in Pyeongchang, the Olympic Athlete from Russia Implementation Group (OARIG) was formed.
This three-person committee, which includes IOC Athletes Commission member Danka Bartekova, IOC Executive Board member Nicole Hoevertsz, and IOC director general Christophe De Kepper, was afforded sole and absolute discretion of removing any proposed names of athletes, officials, and staff considered for invitation. In this case, the athlete’s voice represents one-third of the votes.
In addition, members of the global network of athletes’ representatives were also able to offer their thoughts on the matter in a conference call earlier this year. The IOC asserts athletes have been involved in “every step of the process,” determining which athletes from Russia should be allowed to compete in Pyeongchang while ensuring fairness was demonstrated.
This interest in the well-being of athletes is not limited to the Pyeongchang Games. The IOC supports an Olympic Study Centre grant program designed to advance research as it pertains to the Olympic Movement.
Over the years, there has been an increased interest in understanding how the IOC can best serve the needs of athletes — both while they are competing and following retirement. One field of interest in the 2018 grant involves examining the IOC’s historical and future support of Olympians.
Similarly, the organizing committee of the 2020 Summer Olympics in Tokyo has said one of its objectives is to be an athlete-centered games. Recognizing the importance of the athletes’ experience in delivering a successful event, the IOC’s Athlete’s Commission will advise the organizing committee on various aspects of the games. This can include the layout of the athletes’ village, the food provided, the location of venues, and the scheduling of events. This list is endless and the rewards invaluable. What is most important here is that athletes’ perspectives are heard and valued.
















 Screenshots of the man talking to the camera and with his momTikTok |
Screenshots of the man talking to the camera and with his momTikTok |  Screenshots of the bakery Image Source: TikTok |
Screenshots of the bakery Image Source: TikTok | 
 A woman hands out food to a homeless personCanva
A woman hands out food to a homeless personCanva A female artist in her studioCanva
A female artist in her studioCanva A woman smiling in front of her computerCanva
A woman smiling in front of her computerCanva  A woman holds a cup of coffee while looking outside her windowCanva
A woman holds a cup of coffee while looking outside her windowCanva  A woman flexes her bicepCanva
A woman flexes her bicepCanva  A woman cooking in her kitchenCanva
A woman cooking in her kitchenCanva  Two women console each otherCanva
Two women console each otherCanva  Two women talking to each otherCanva
Two women talking to each otherCanva  Two people having a lively conversationCanva
Two people having a lively conversationCanva  Two women embrace in a hugCanva
Two women embrace in a hugCanva 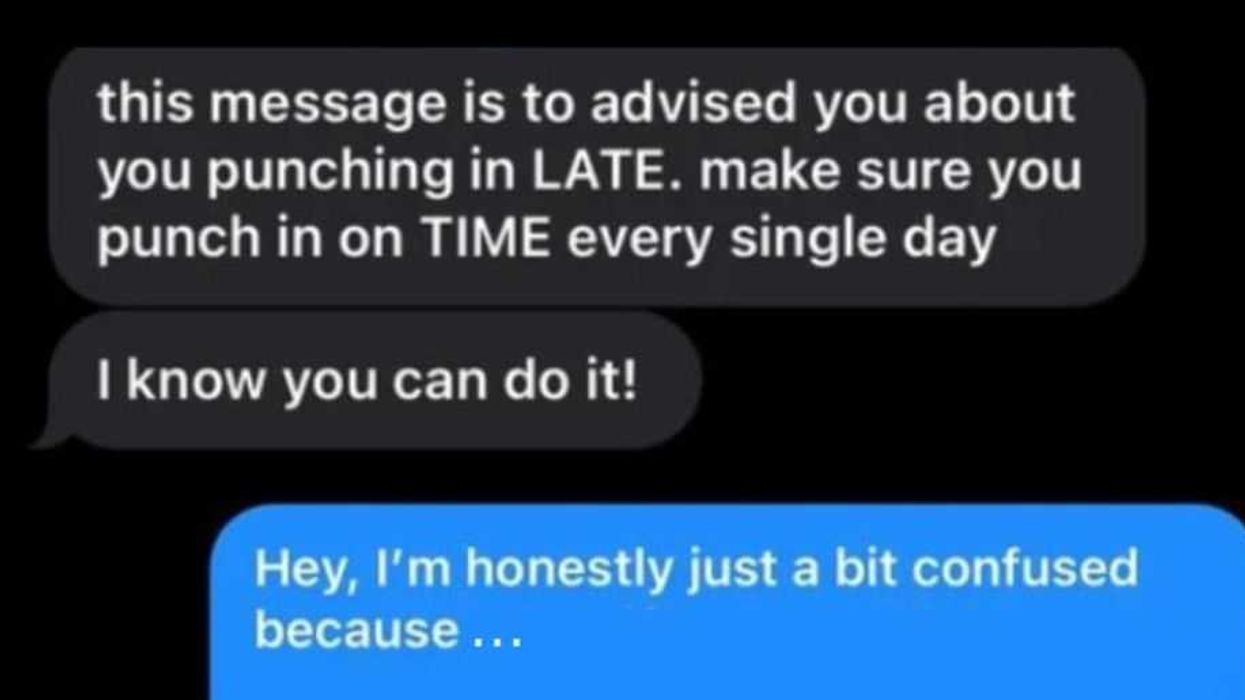
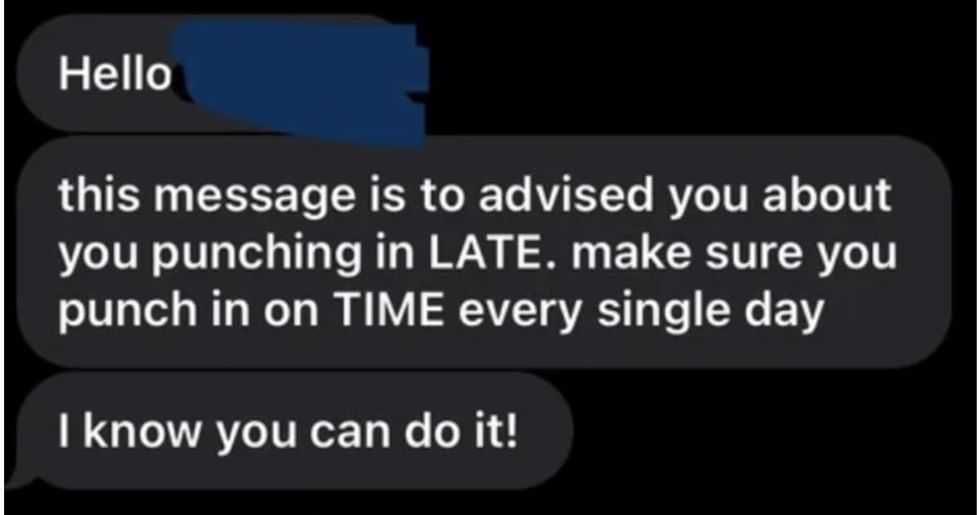 A reddit commentReddit |
A reddit commentReddit | 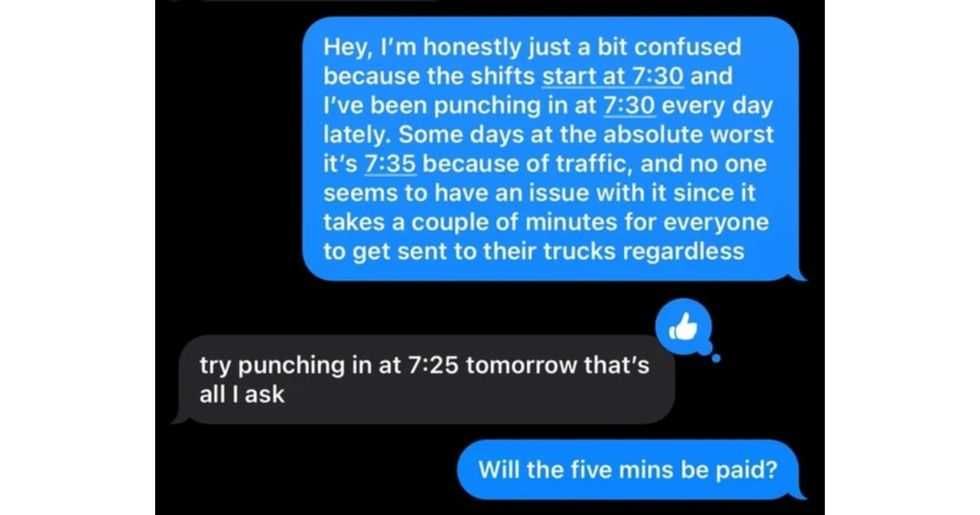 A Reddit commentReddit |
A Reddit commentReddit | 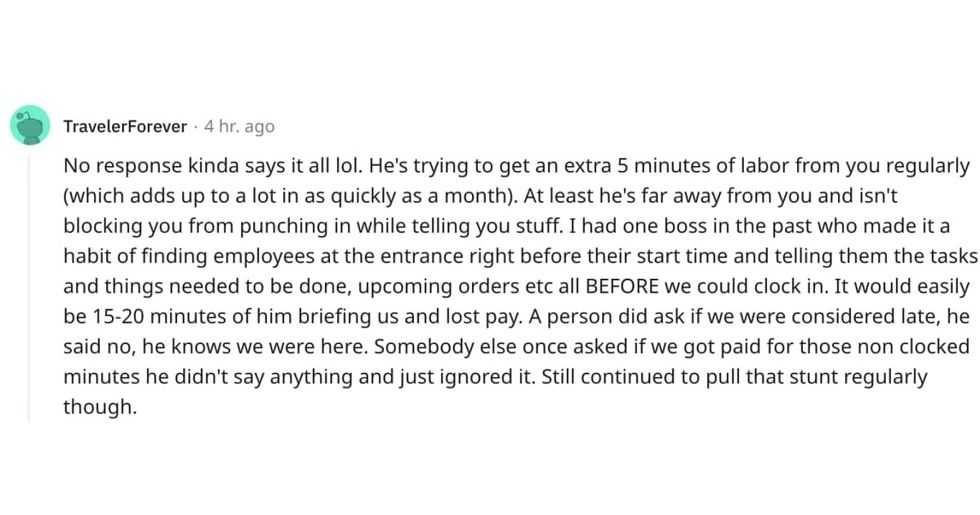 A Reddit commentReddit |
A Reddit commentReddit |  Stressed-out employee stares at their computerCanva
Stressed-out employee stares at their computerCanva
 Who knows what adventures the bottle had before being discovered.
Who knows what adventures the bottle had before being discovered. 
 Gif of young girl looking at someone suspiciously via
Gif of young girl looking at someone suspiciously via 
 A bartender makes a drinkCanva
A bartender makes a drinkCanva