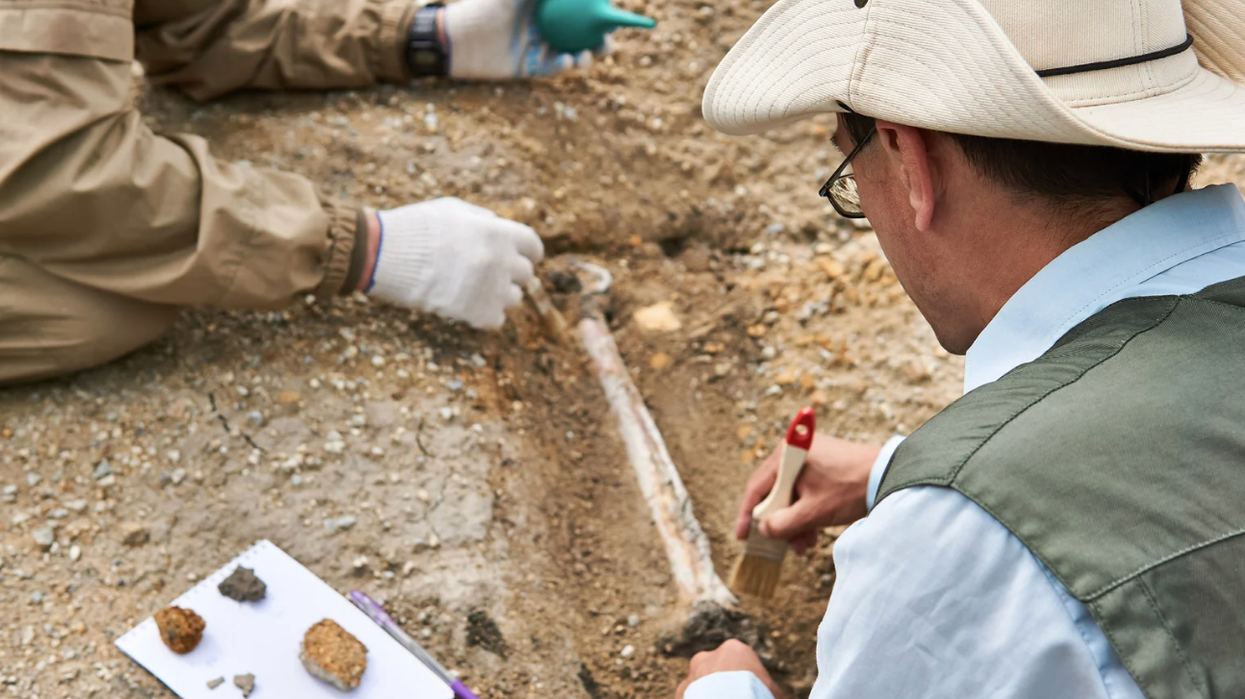
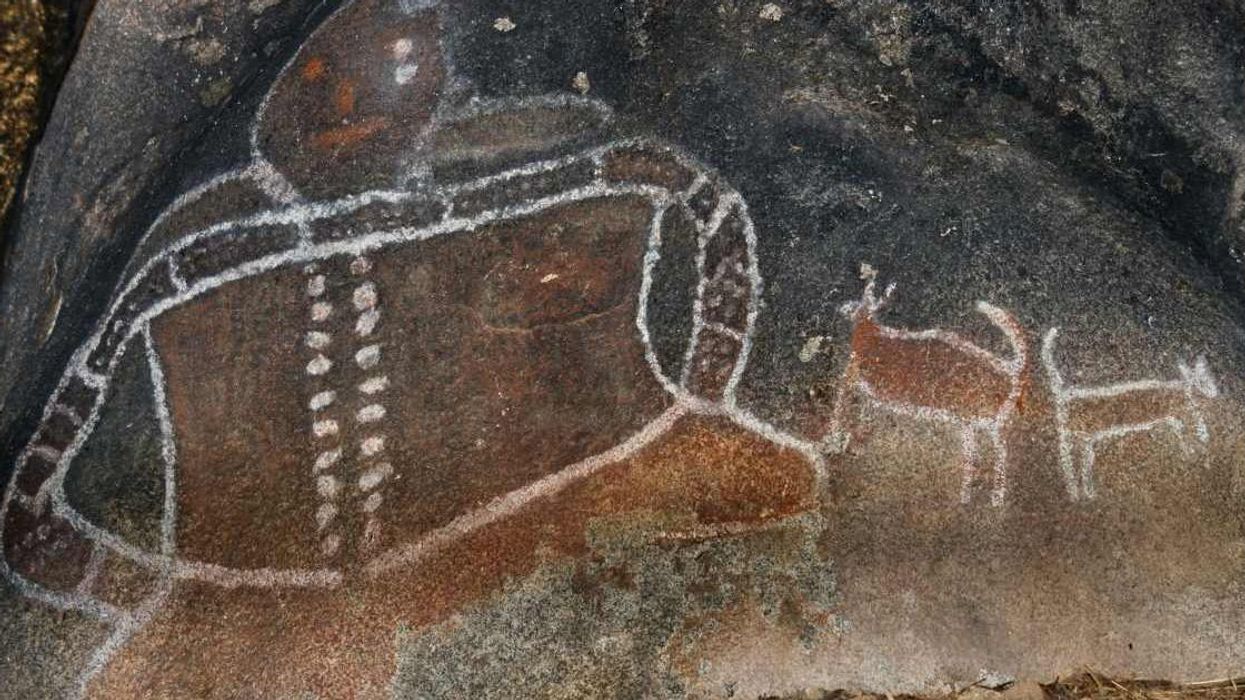
Located atop Karampuang hill in Indonesia is Leang Karampuang cave which is ornamented by limestone formations formed over thousands of years of erosion. As one arrives at this cave, making their way through the rainforests in the Maros-Pangkep region of South Sulawesi, one will find what is now known as the “oldest cave art in the world” imprinted on a karst ceiling. In a new study, published in journal Nature, researchers have identified this cave art as “the earliest known surviving example of representational art and visual storytelling in the world.” The ancient painting portrays three humanlike figures interacting with a wild pig and it is believed that the art was not made by modern humans.
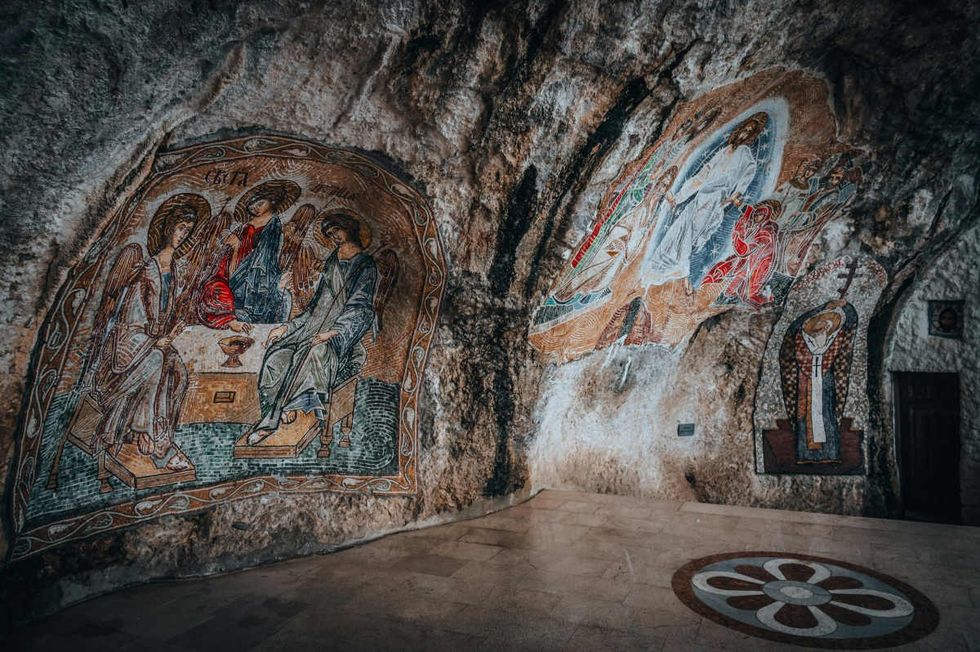

From previous studies, researchers knew that Sulawesi is home to some of the earliest cave art in the world, they note in the paper. They tested the paintings using “solution uranium-series (U-series) analysis” of calcite deposits overlying rock art in Sulawesi’s limestone caves. This time, they used a more advanced and novel method called “laser-ablation U-series imaging” to re-date some of the earliest cave art in this karst area and more accurately unfold the artworks’ ages.
Through this latest method, they re-dated a painting first found in the Leang Bulu’ Sipong 4 cave. The painting depicted a hunting scene with figures interpreted as therianthropes (part-human, part-animal beings) hunting warty pigs and dwarf buffalo. It was earlier dated to a minimum of 43,900 thousand years. With the imaging approach, scientists discovered that this painting was at least 4,040 years older than previously thought.
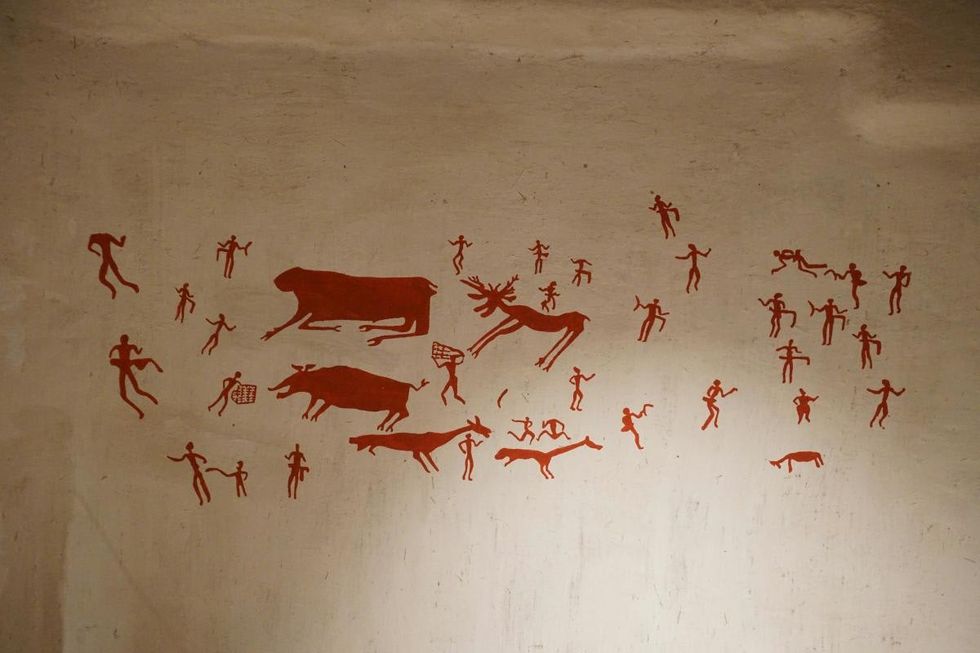
They extended the imaging approach to the artwork found in Leang Karampuang cave by dating tiny layers of calcium carbonate that had formed on top of the art. Their analysis revealed that the underlying artwork, colored in red-hued pigment, was painted at least 51,200 years ago, making it the oldest known reliably dated cave painting in the world, and the earliest narrative art found anywhere. This also suggested that the art was probably created by our ancient hominin cousins, who existed during this timeline, rather than evolved humans.

This advanced dating method was co-developed by archaeology specialists Professor Maxime Aubert and his colleague, Professor Renaud Joannes-Boyau. Talking about this method, Professor Aubert said, “It will revolutionize rock art dating,” per the university press release. “The innovative technique we’ve pioneered enables us to create detailed ‘maps’ of calcium carbonate layers. This capability empowers us to pinpoint and steer clear of regions affected by natural diagenesis processes, which stem from intricate growth histories. Consequently, our age determinations for rock art become more robust and dependable,” said Professor Joannes-Boyau.
The research was collectively conducted by a team of scientists, co-led by researchers from Australia’s Griffith University, the Indonesian National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), and Southern Cross University, according to the press release. The team was led by an Indonesian rock art specialist Adhi Agus Oktaviana. “Our results are very surprising,” said Oktaviana in the press release, and added, “This is the first time rock art dates in Indonesia have ever been pushed beyond the 50,000-year mark.”

Professor Adam Brumm, who co-authored the study, said that the cave art from Leang Karampuang and Leang Bulu’ Sipong 4 casts new light on the important role of storytelling in the history of art. “It is noteworthy that the oldest cave art we have found in Sulawesi thus far consists of recognizable scenes: that is, paintings that depict humans and animals interacting in such a way that we can infer the artist intended to communicate a narrative of some kind – a story.”
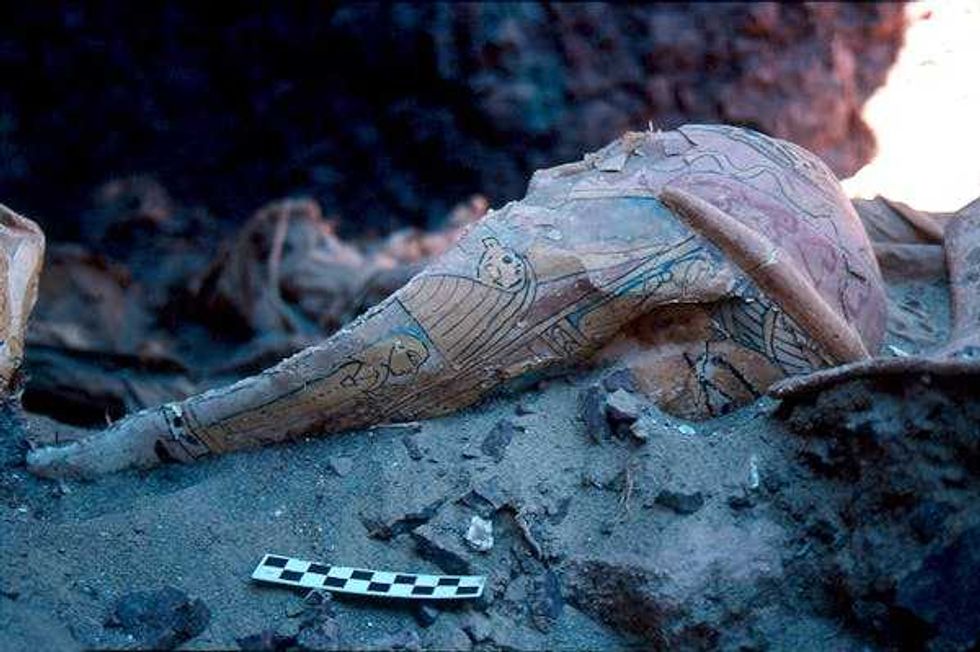














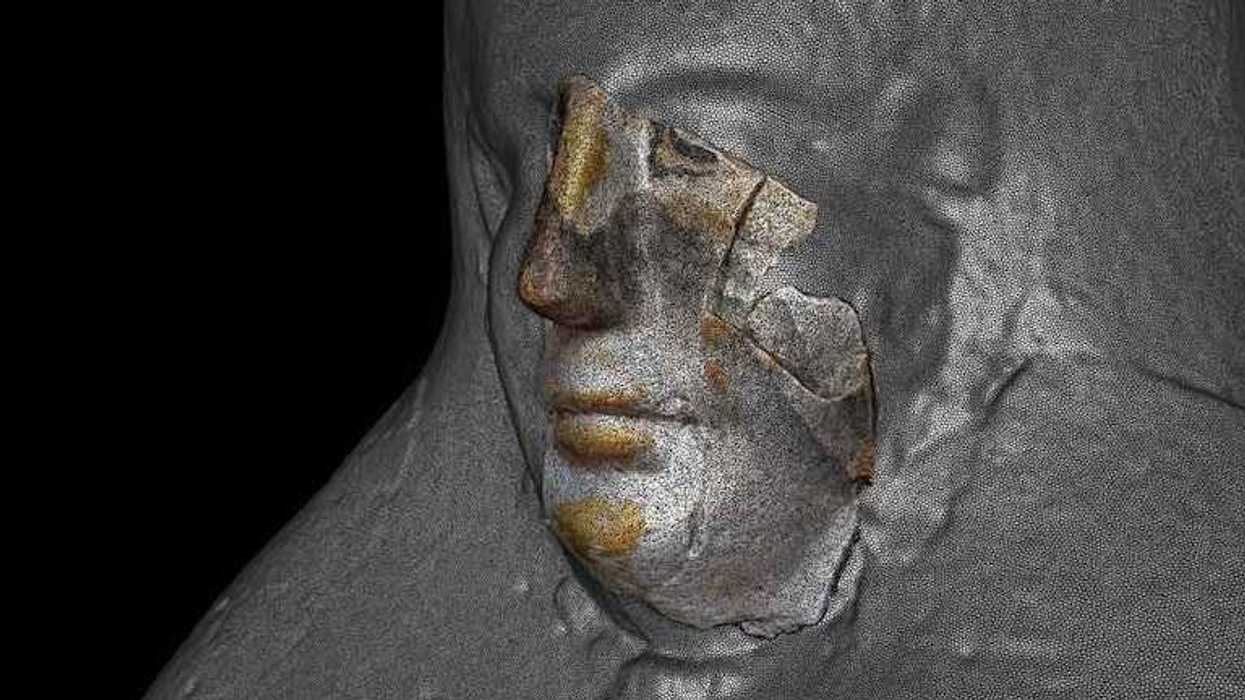
 Reuse over time and looting shifted and damaged the contents of an ancient Egyptian tomb. This displaced mummy mask could have a relationship to other artifacts already in museums around the world.Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo
Reuse over time and looting shifted and damaged the contents of an ancient Egyptian tomb. This displaced mummy mask could have a relationship to other artifacts already in museums around the world.Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo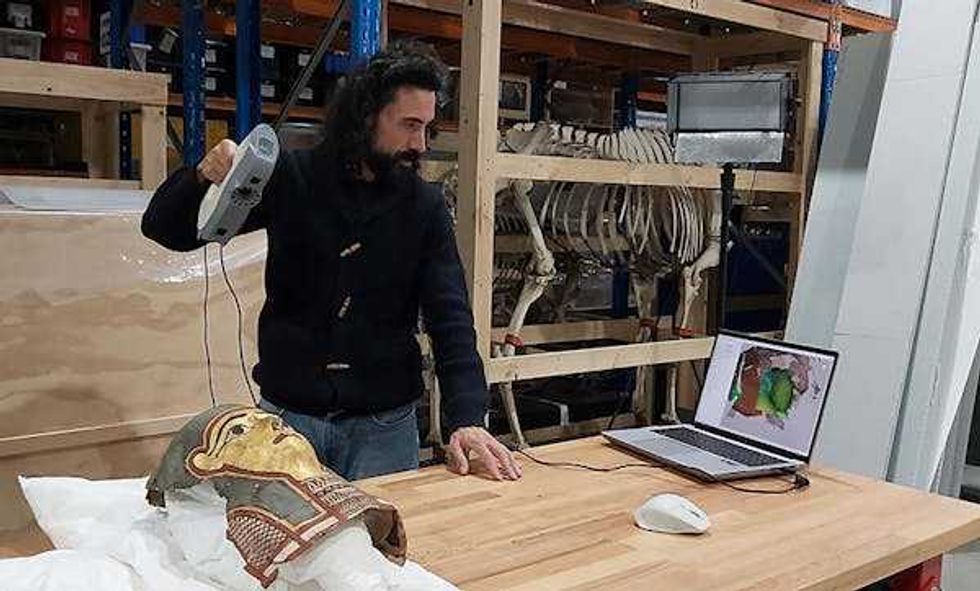 Archaeologists can use handheld 3D scanners to noninvasively map objects in very fine detail.Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo
Archaeologists can use handheld 3D scanners to noninvasively map objects in very fine detail.Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo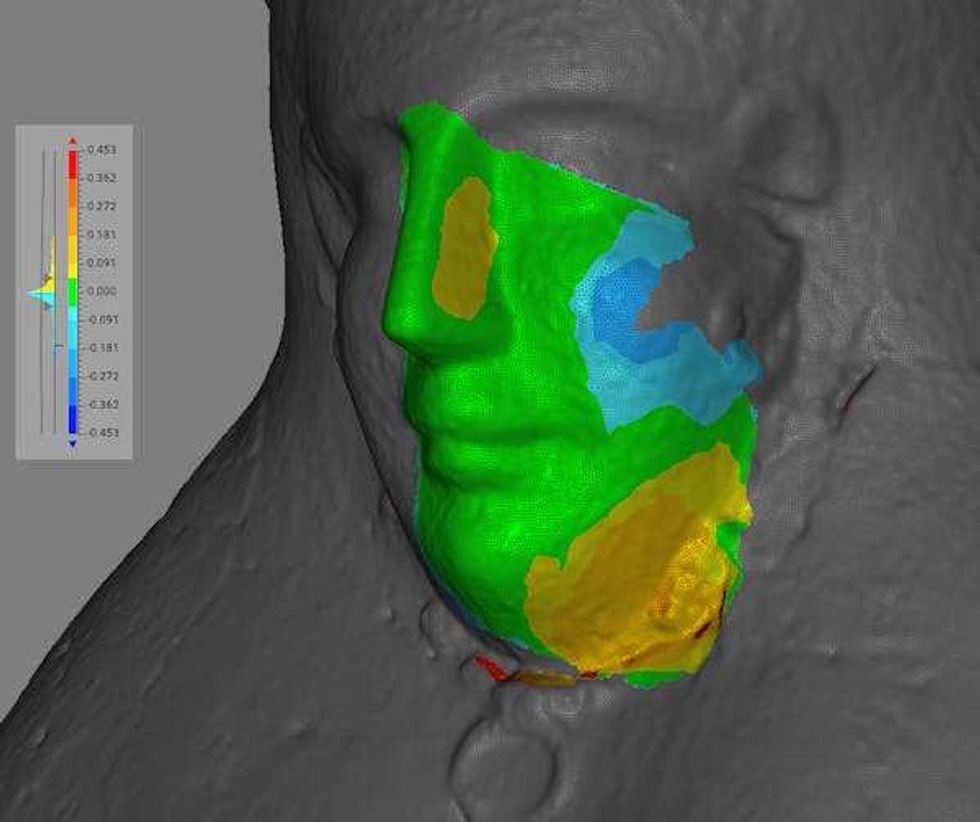 The mask reference surface is shown in gray, while the aligned fragment is colored based on the surface-to-surface distance at each point. Green indicates a good match with almost no distance. Cooler colors show areas where the fragment lies below the reference mask, and warmer colors show where it lies above.Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo
The mask reference surface is shown in gray, while the aligned fragment is colored based on the surface-to-surface distance at each point. Green indicates a good match with almost no distance. Cooler colors show areas where the fragment lies below the reference mask, and warmer colors show where it lies above.Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo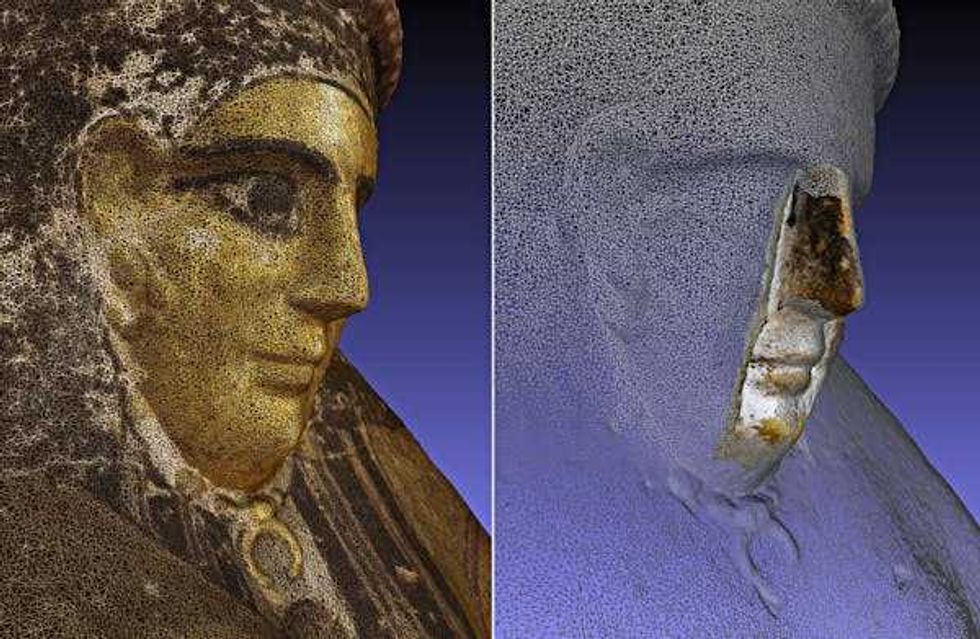 The mask fragment was a very close match to a complete mask, suggesting they were made in the same mold.Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo
The mask fragment was a very close match to a complete mask, suggesting they were made in the same mold.Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo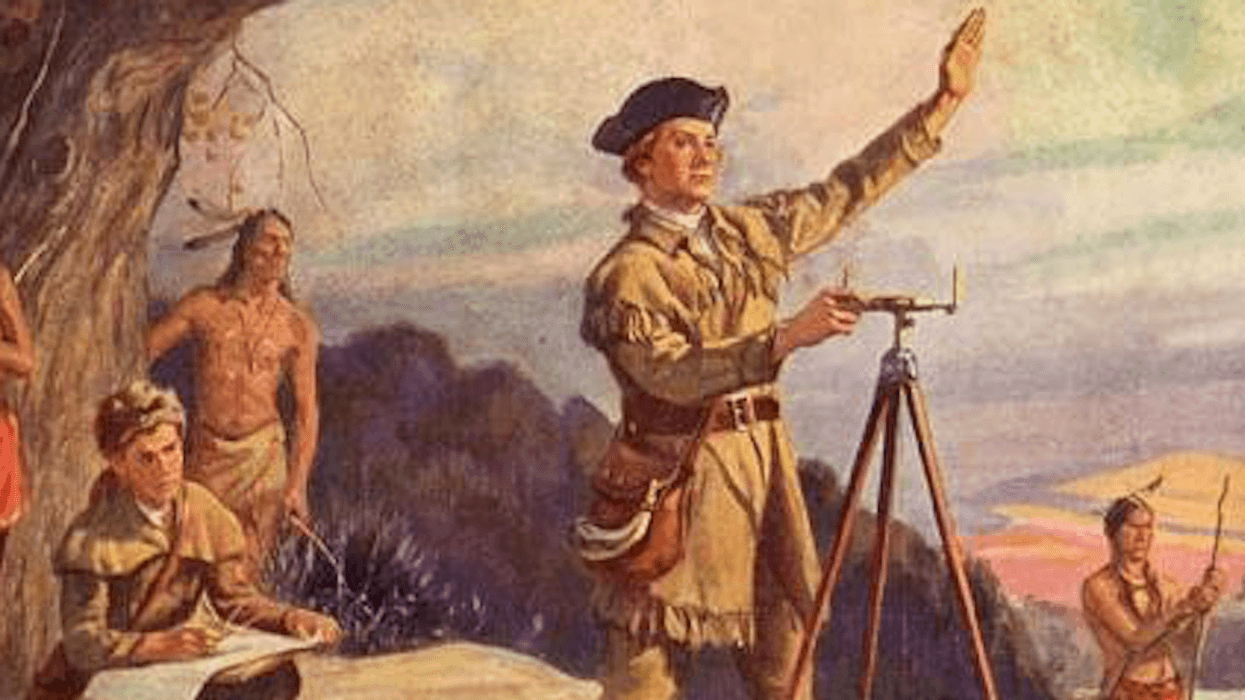
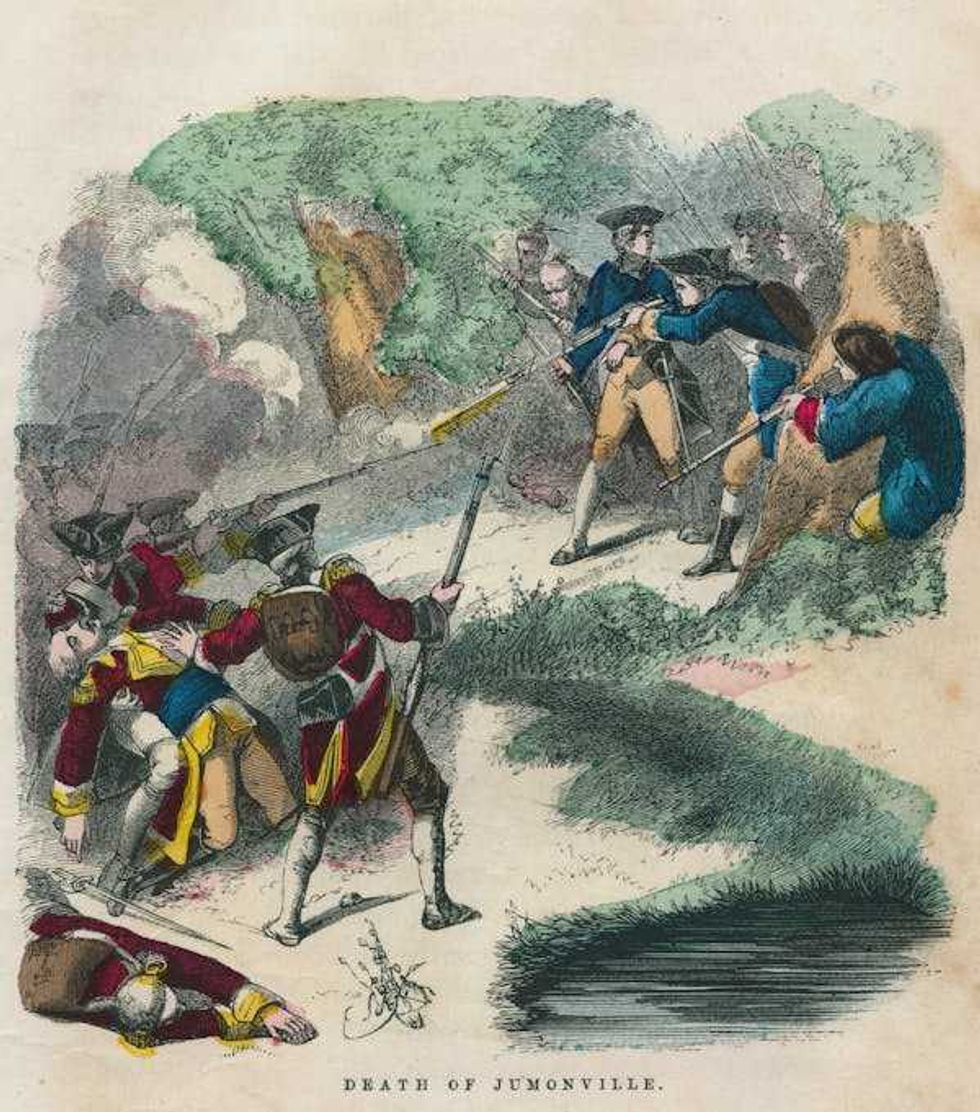 The Jumonville affair became the opening battle of the French and Indian War.
The Jumonville affair became the opening battle of the French and Indian War.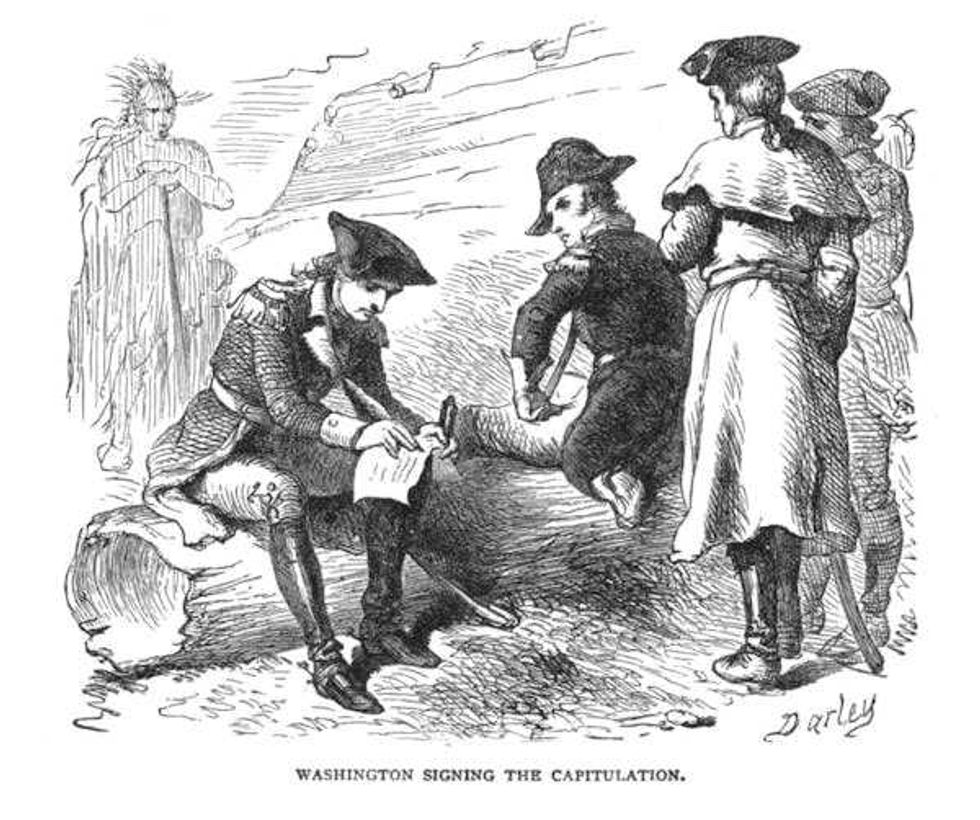 Washington was outnumbered and outmaneuvered at Fort Necessity.
Washington was outnumbered and outmaneuvered at Fort Necessity.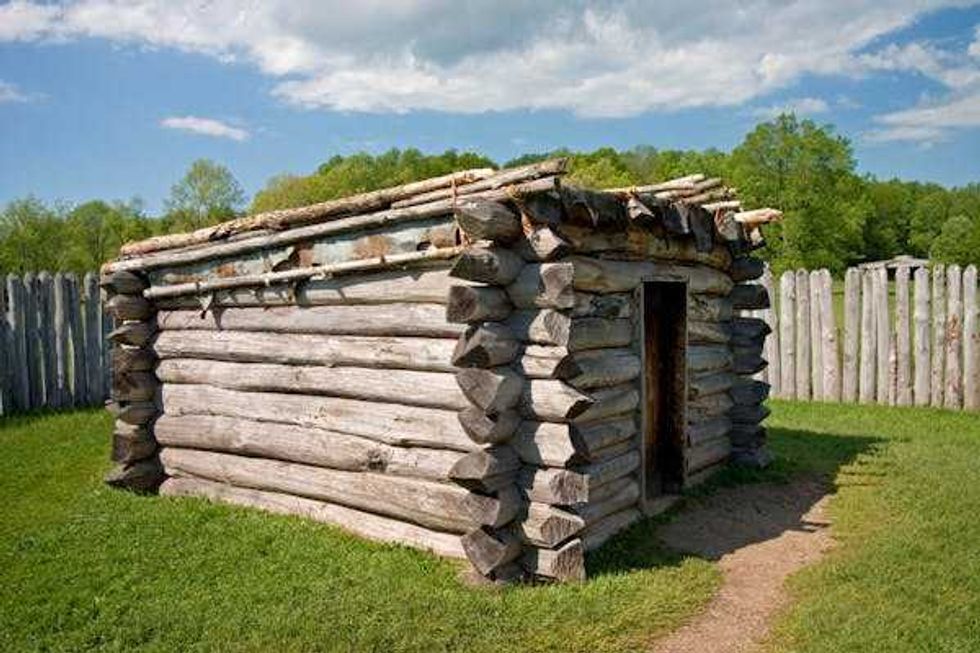 A log cabin used to protect the perishable supplies still stands at Fort Necessity today.
A log cabin used to protect the perishable supplies still stands at Fort Necessity today.
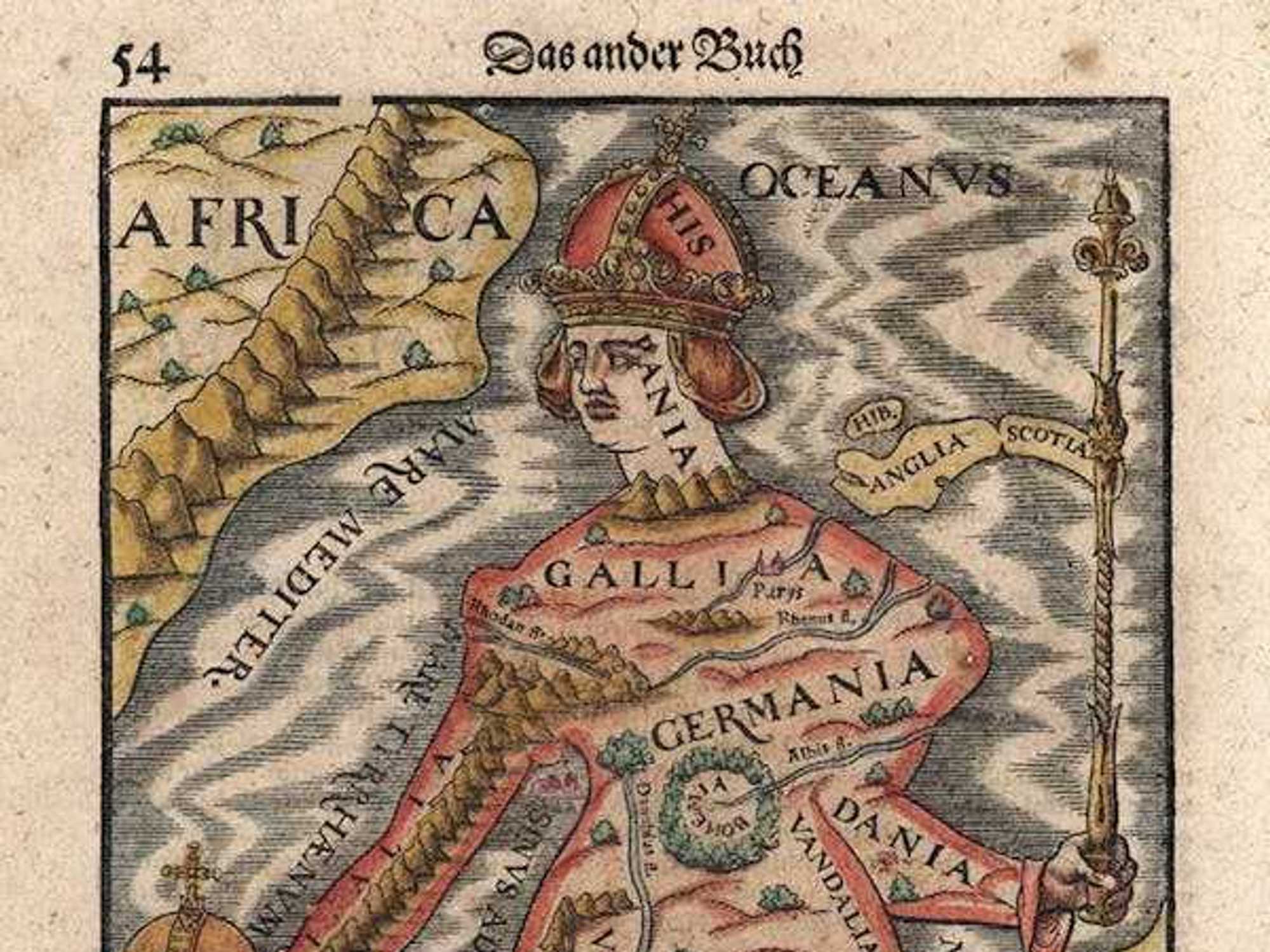 Europa Regina (1570).
Europa Regina (1570).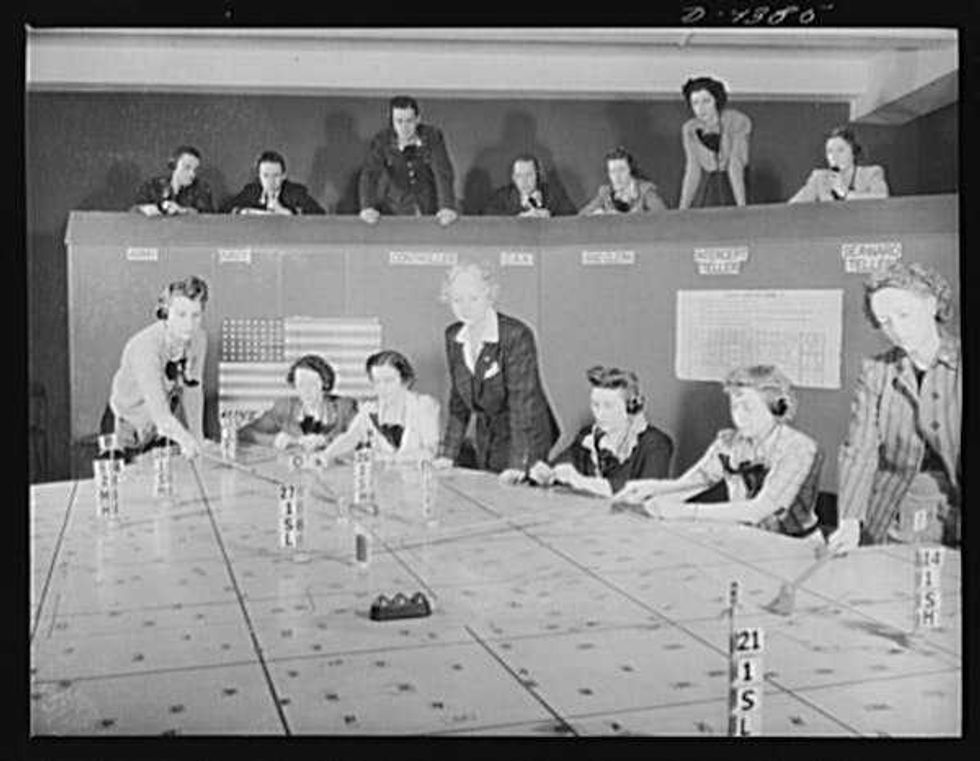 The ‘Military Mapping Maidens’ created tens of thousands of maps during World War II.
The ‘Military Mapping Maidens’ created tens of thousands of maps during World War II.
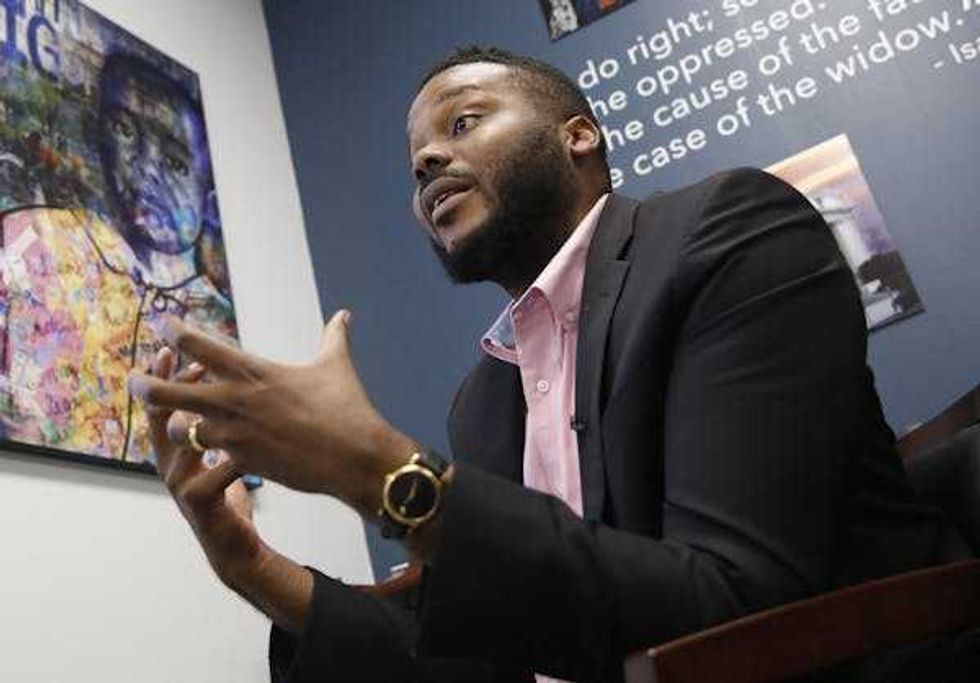 As mayor of Stockton, Calif., Michael Tubbs ran a pioneering program that provided a basic income to a limited number of residents.
As mayor of Stockton, Calif., Michael Tubbs ran a pioneering program that provided a basic income to a limited number of residents. Martin Luther King Jr. believed Americans of different racial backgrounds could coalesce around shared economic interests.
Martin Luther King Jr. believed Americans of different racial backgrounds could coalesce around shared economic interests.
 It's difficult to imagine seeing a color and not having the word for it. Canva
It's difficult to imagine seeing a color and not having the word for it. Canva
 Sergei Krikalev in space.
Sergei Krikalev in space. 