About 4.6 billion years ago, the formation of the solar system left behind solid debris tumbling through space. These remnants, known as “asteroids,” typically orbit the Sun and are concentrated in the asteroid belt between Jupiter and Mars. However, Jupiter’s gravity occasionally pulls an asteroid from its path, sending it hurtling through the solar system—sometimes toward Earth.

Since a mountain-sized asteroid wiped out the dinosaurs 66 million years ago, Earth has not experienced a major impact event. However, in a 2007 interview with Conan O’Brien, astrophysicist Neil deGrasse Tyson made a chilling prediction. He warned that a massive asteroid named “Apophis” could potentially collide with Earth in 2029, a prediction that continues to resurface in discussions today.
Tyson estimated that Apophis will get close to the Earth on April 13, 2029, and will dip even lower than most of the Earth’s communication satellites. It will be the “biggest closest thing known to come near the Earth,” he described. The communication satellites, Tyson explained, are geosynchronous orbits about 23,000 miles up. “This [Apophis] will come around 18,000 miles,” he said, and revealed that, “It will be visible from northern Europe.” According to Tyson, this asteroid approaching the planet will look like a “fast-moving bright object across the night sky, moving at about, probably 10 miles per second.”
First discovered in 2004, the Apophis was identified as “one of the most hazardous asteroids that could impact Earth,” according to NASA. This treacherous celestial object looks like a “two-lobed peanut.” Surprisingly, the size of this asteroid is not a major issue. According to NASA, it is only 1,100 feet (340 meters) in width.

However, since the time of its discovery, it has been considered a major threat to the planet. Tyson said that the threat is depicted in its name itself. Apophis is named after the Egyptian god of death and darkness, which, he said, illustrates how dangerous it could be for humans. If it was not considered dangerous, scientists would have never named it “Apophis,” but rather a regular name like Bambi, Tiffany, or Fredy.
“Its orbit remains sufficiently uncertain,” Tyson explained and added that if Apophis enters the “Keyhole,” which is a range of about 600 to 700 miles, then Earth’s gravity will be just right, or rather just wrong. “It will alter its orbit so it will hit us seven years later.” However, the likelihood of the asteroid making its way through the Keyhole is several in a million, he said.
However, NASA reports that after a March 2021 radar-observation campaign, scientists have assured that there is no risk of Apophis impacting Earth for at least a century. At this time, when Apophis flitted past the Earth at a safe distance, scientists used high-powered radar instruments to calculate the estimate of its orbit around the Sun. They concluded that the asteroid won’t impact the Earth anytime before 2068. NASA’s “Asteroid Watch,” which tracks and detects asteroids, will also send a spacecraft to study Apophis during its 2029 temporary flyby. So the question of whether Apophis will collide with the planet or not, cannot be answered definitely until 2029.
@jdunbar0 #apophis #asteroid #solareclipse
















 Representative Image: Accents reveal heritage and history.
Representative Image: Accents reveal heritage and history.  Representative Image: Even unseen you can learn a lot from an accent.
Representative Image: Even unseen you can learn a lot from an accent. 
 Rice grain and white rice.Image via
Rice grain and white rice.Image via  Person eats rice.Image via
Person eats rice.Image via  Washing and rinsing rice.
Washing and rinsing rice.  Mother and daughter eating rice meal.Image via
Mother and daughter eating rice meal.Image via 
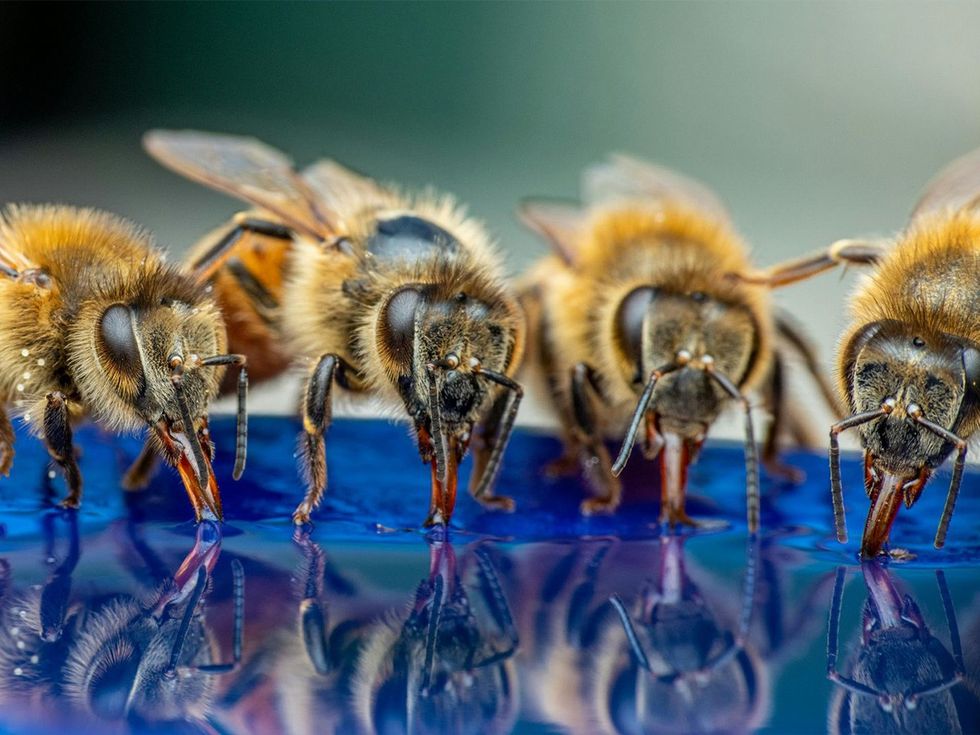
 Bees feeding on food source.Image via
Bees feeding on food source.Image via 
 In the depths...Pexels | francesco ungaro
In the depths...Pexels | francesco ungaro Hope the lights stay on. Pexels | parfait fongang
Hope the lights stay on. Pexels | parfait fongang "That was beyond crazy..." YouTube |
"That was beyond crazy..." YouTube |  "This is the stuff of my nightmares..."YouTube |
"This is the stuff of my nightmares..."YouTube |  "Totally blown away..." YouTube |
"Totally blown away..." YouTube | 
 A representative Image of The Atlantic Ocean. Source: Pexels | Kellie Churchman
A representative Image of The Atlantic Ocean. Source: Pexels | Kellie Churchman Representative Image Source: Painting from a series by Ernest Untermann in the museum at Dinosaur National Monument, Utah.
Representative Image Source: Painting from a series by Ernest Untermann in the museum at Dinosaur National Monument, Utah. Representative Image Source: VARIOUS DINOSAURS IN GOBI DESERT. Photo by H. Armstrong Roberts/ClassicStock/Getty Images
Representative Image Source: VARIOUS DINOSAURS IN GOBI DESERT. Photo by H. Armstrong Roberts/ClassicStock/Getty Images
President Donald J. Trump and photo of a forest.
Public united and adamantly opposes Trump’s plan to roll back the Roadless Rule
There doesn't seem to be much agreement happening in the U.S. right now. Differing moral belief systems, economic disparity, and political divide have made a country with so many positives sometimes feel a little lost. Everyone desperately seeks a niche, a connection, or a strong sense of community to which they can feel a "part of," rather than just "apart."
But there seems to be one thing that the country strongly unites over, and that's the "Roadless Rule." With the Trump Administration attempting to roll back conservation policies that protect U.S. National Forests, Americans are saying in harmony an emphatic "No." A nonpartisan conservation and advocacy organization, the Center for Western Priorities, reviewed a comment analysis on the subject. After receiving 223,862 submissions, a staggering 99 percent are opposed to the president's plan of repeal.
What is the 'Roadless Rule' policy implemented in 2001?
The Roadless Rule has a direct impact on nearly 60 million acres of national forests and grasslands. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the rule prohibits road construction and timber harvests. Enacted in 2001, it is a conservation rule that protects some of the least developed portions of our forests. It's considered to be one of the most important conservation wins in U.S. history.
America's national forests and grasslands are diverse ecosystems, timeless landscapes, and living treasures. They sustain the country with clean water and the wood products necessary to build our communities. The National Parks protected under their umbrella offer incredible recreational retreats and outdoor adventure.
Why does the administration want to roll it back?
U.S. Secretary of Agriculture Brooke L. Rollins told the Department of Agriculture in a 2025 press release, “We are one step closer to common sense management of our national forest lands. Today marks a critical step forward in President Trump’s commitment to restoring local decision-making to federal land managers to empower them to do what’s necessary to protect America’s forests and communities from devastating destruction from fires." Rollins continued, “This administration is dedicated to removing burdensome, outdated, one-size-fits-all regulations that not only put people and livelihoods at risk but also stifle economic growth in rural America. It is vital that we properly manage our federal lands to create healthy, resilient, and productive forests for generations to come. We look forward to hearing directly from the people and communities we serve as we work together to implement productive and commonsense policy for forest land management.”
Forest Service Chief Tom Schultz explained the Roadless Rule frustrated land management and acts as a challenging barrier to action. It prohibits road construction needed to navigate wildfire suppression and properly maintain the forest. Schultz said, “The forests we know today are not the same as the forests of 2001. They are dangerously overstocked and increasingly threatened by drought, mortality, insect-borne disease, and wildfire. It’s time to return land management decisions where they belong – with local Forest Service experts who best understand their forests and communities."
Why are people adamantly opposed to the proposed rollback?
A 2025 article in Earthjustice, a nonprofit environmental law organization, expressed its concern over the protection of national forests covering 36 states and Puerto Rico. A rescinded rule allows increased logging, extractive development, and oil and gas drilling in previously undisturbed backcountry. Here is what some community leaders had to say about it:
President Gloria Burns, Ketchikan Indian Community, said, "You cannot separate us from the land. We depend on Congress to update the outdated and predatory, antiquated laws that allow other countries and outside sources to extract our resource wealth. This is an attack on Tribes and our people who depend on the land to eat. The federal government must act and provide us the safeguards we need or leave our home roadless. We are not willing to risk the destruction of our homelands when no effort has been made to ensure our future is the one our ancestors envisioned for us. Without our lungs (the Tongass) we cannot breathe life into our future generations.”
Linda Behnken, executive director of the Alaska Longline Fishermen’s Association, stated, "Roadbuilding damaged salmon streams in the past — with 240 miles of salmon habitat still blocked by failed road culverts. The Roadless Rule protects our fishing economy and more than 10,000 jobs provided by commercial fishing in Southeast Alaska.”
The Sierra Club's Forest Campaign Manager Alex Craven seemed quite upset, saying, "The Forest Service followed sound science, economic common sense, and overwhelming public support when they adopted such an important and visionary policy more than 20 years ago. Donald Trump is making it crystal clear he is willing to pollute our clean air and drinking water, destroy prized habitat for species, and even increase the risk of devastating wildfires, if it means padding the bottom lines of timber and mining companies.”
The 2025 recession proposal would apply to nearly 45 million acres of the national forests. With so many people writing in opposition to the consensus, the public has determined they don't want it to happen.
Tongass National Forest is at the center of the Trump administration's intention to roll back the 2001 Roadless Rule. You can watch an Alaska Nature Documentary about the wild salmon of Tongass National Forrest here:
- YouTube www.youtube.com
The simple truth is we elect our public officials to make decisions. The hope is they do this for all of our well-being, although often it seems they do not. Even though we don't have much power to control what government officials do, voicing our opinions strongly enough often forces them to alter their present course of action. With a unanimous public voice saying, "No!" maybe this time they will course correct as the public wishes.