Over the past few years, the devastating effects of the anti-vaxxer movement have become apparent. The disinformation spread by people who believe that vaccines are dangerous and cause autism led to a historic measles outbreak in the U.S. in 2019.
A recent poll found the number of Americans who believe that "it is extremely or very important that parents vaccinate their children" has dropped by 10% since 2001. Currently, 84% of Americans believe it's important to have their children vaccinated.
The anti-vaxxer movement is growing despite the fact there have been over 140 peer-reviewed articles, published in relatively high impact factor or specialized journals that document the lack of a correlation between autism and vaccines.
The need to combat the disinformation spread by anti-vaxxers has become even more important in the COVID-19 era. Reports from major pharmaceutical companies there could be a COVID-19 vaccine ready by within the next few months.
An effective vaccine would help stop the virus that's claimed over 200,00 American lives and help get the economy back on track. But if Americans are hesitant to take the vaccine due to disinformation from anti-vaxxers, the virus could continue to spread indefinitely.
A recent poll found that 35% of Americans wouldn't take a COVID-19 vaccine. Sixty percent said they would and 5% are unsure. Democrats were also more likely to be willing to take the vaccine than Republicans, 71% to 48%.
Earlier this month, Republican senator Mitt Romney of Utah called for an "aggressive campaign" to counter anti-vaxxer disinformation on vaccines.
"There are literally books out there written to describe why vaccines are bad," the Utah Republican said at a Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee hearing." And I wonder if it does not make sense for our government to put out a very comprehensive effort to dispel this growing sense of vaccines being bad."
"I don't know how you do that, but it would come to mind that you are doing that with regards to tobacco and massive advertising on TV," the senator continued. "You could have debates, you could call in these people who write these books and have discussions with them, which are publicized. You could have a much more aggressive campaign on social media."
NIH director Dr. Francis Collins responded to Romney's suggestion saying the situation causes "anger" and "frustration" that this "kind of misinformation is so readily spread by people who have another agenda."
Romney should be all too familiar with the thread caused by anti-vaxxers. Utah has rated in the bottom ten of states in the DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis), polio, H. influenzae type B, as well as 4, 5 and 7-vaccine series among 19- to 35-month-olds.
The Public Library of Science Medicine rated Salt Lake City and Provo as hotspots for anti-vaccination.
If the government hopes to reverse the growth of the anti-vaxxer movement, it better move quickly. It's been growing even faster than ever due to the COVID-19 pandemic. More people have fallen for anti-vaxxer rhetoric due to their mistrust of president Trump on vaccines, the growing Q Anon conspiracy, and skepticism over the speed in which a potential vaccine can be developed.
"Anti-vaccination sentiment is going into the mainstream," Heidi Larson, director of the Vaccine Confidence Project at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, told the Los Angeles Times. "A lot of people you never would have imagined are now saying that maybe the anti-vaccination lobby has a point."















 What foods would you pick without diet culture telling you what to do?
What foods would you pick without diet culture telling you what to do?  Flexibility can help you adapt to – and enjoy – different food situations.
Flexibility can help you adapt to – and enjoy – different food situations.
 Anxious young woman in the rain.Photo credit
Anxious young woman in the rain.Photo credit  Woman takes notes.Photo credit
Woman takes notes.Photo credit 
 Revenge can feel easier than forgiveness, which often brings sadness or anxiety.
Revenge can feel easier than forgiveness, which often brings sadness or anxiety.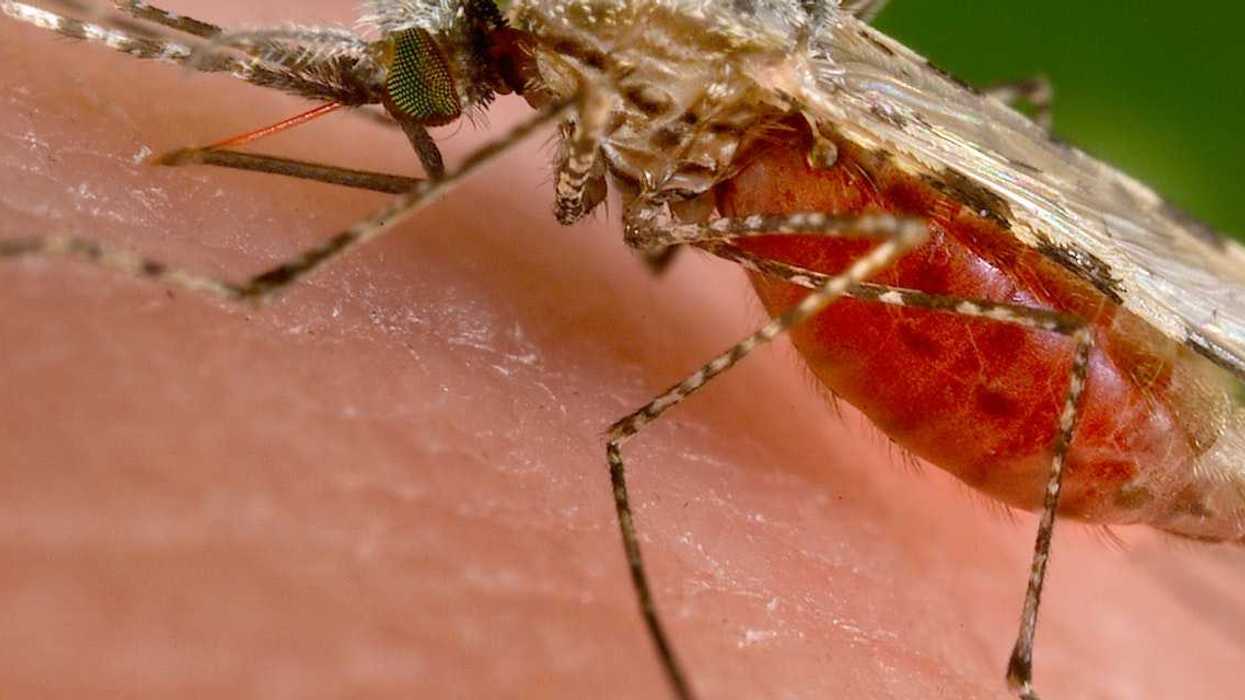 
 In the past two years, two malaria vaccines have become available for babies starting at 5 months of age.
In the past two years, two malaria vaccines have become available for babies starting at 5 months of age. By exploiting vulnerabilities in the malaria parasite’s defense system, researchers hope to develop a treatment that blocks the parasite from entering cells.
By exploiting vulnerabilities in the malaria parasite’s defense system, researchers hope to develop a treatment that blocks the parasite from entering cells.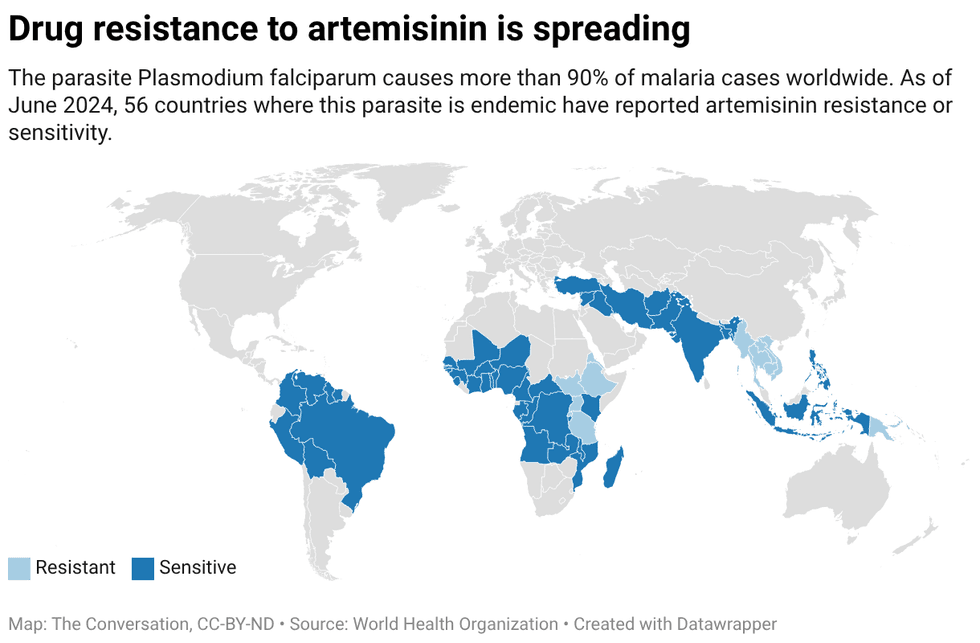 Created with
Created with