It seems like nearly every day brings the promise of some medical miracle on the horizon: cures for disease, breakthrough diets and so on. But who would have thought that in 2017 scientists would be announcing the discovery of a previously unknown human organ?
Well, that’s just what happened. A new paper in the journal The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology explains that the newly classified organ, the mesentery, had been hiding in plain sight in our digestive systems for more than 100 years.
"In the paper, which has been peer reviewed and assessed, we are now saying we have an organ in the body which hasn’t been acknowledged as such to date," researcher J Calvin Coffey, who made the discovery, writes. "The anatomic description that had been laid down over 100 years of anatomy was incorrect. This organ is far from fragmented and complex. It is simply one continuous structure."
Now, official medical books are literally being re-written to include the new organ, which had previously been believed to simply contain fragments from other organs.
And beyond just being an incredibly cool discovery, Coffey says that medical students are now formally studying the still little-understood organ, opening up potential for new disease treatments.
"Now we have established anatomy and the structure. The next step is the function. If you understand the function you can identify abnormal function, and then you have disease. Put them all together and you have the field of mesenteric science … the basis for a whole new area of science," he said.
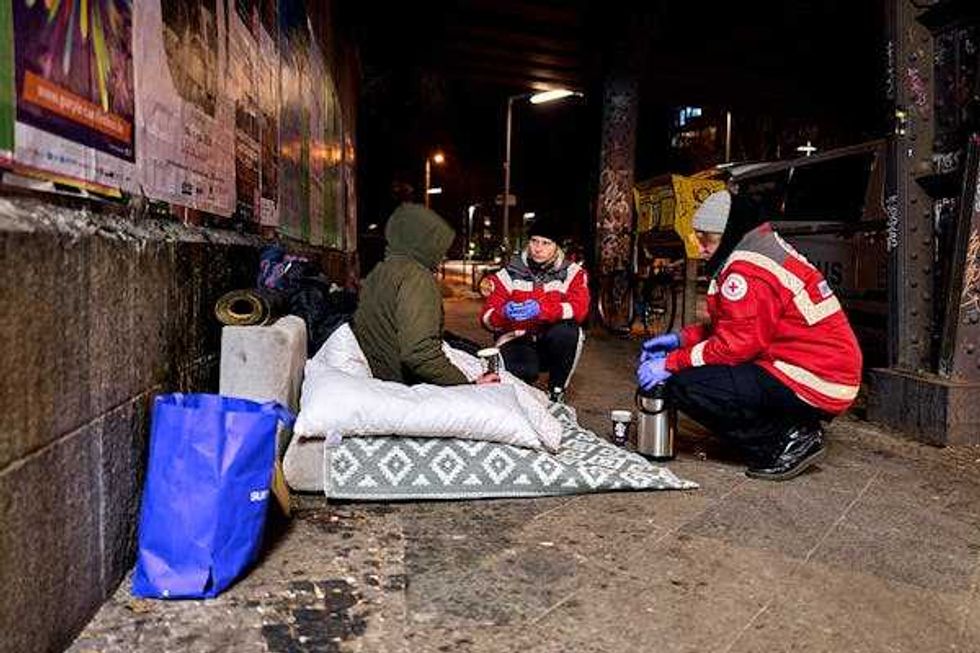













 Volunteers who drive homeless people to shelters talk with a person from Ukraine in Berlin on Jan. 7, 2026.
Volunteers who drive homeless people to shelters talk with a person from Ukraine in Berlin on Jan. 7, 2026.
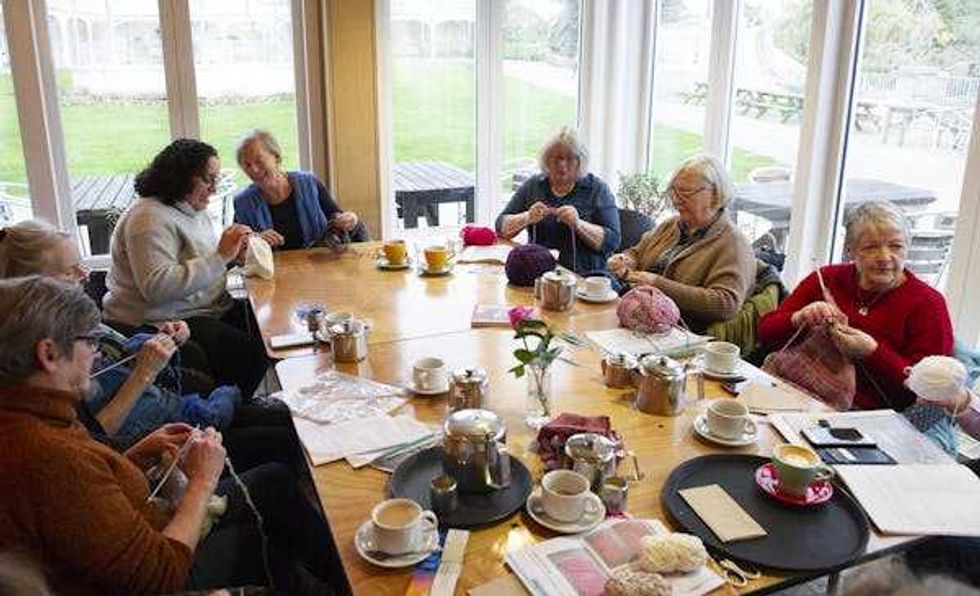 Tasks that stretch your brain just beyond its comfort zone, such as knitting and crocheting, can improve cognitive abilities over your lifespan – and doing them in a group setting brings an additional bonus for overall health.
Tasks that stretch your brain just beyond its comfort zone, such as knitting and crocheting, can improve cognitive abilities over your lifespan – and doing them in a group setting brings an additional bonus for overall health.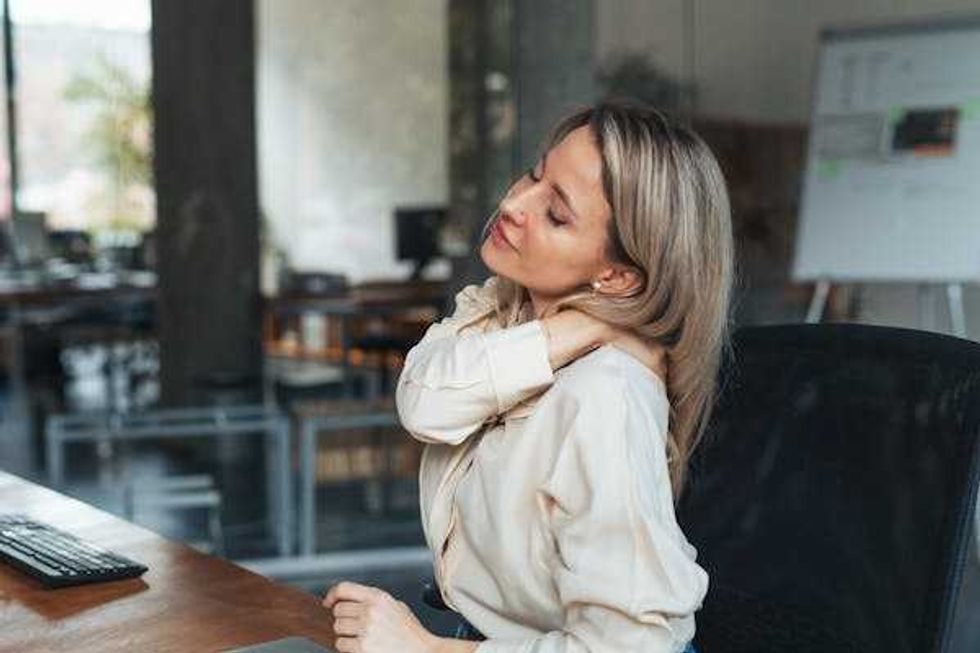 Overdoing any task, whether it be weight training or sitting at the computer for too long, can overtax the muscles as well as the brain.
Overdoing any task, whether it be weight training or sitting at the computer for too long, can overtax the muscles as well as the brain.
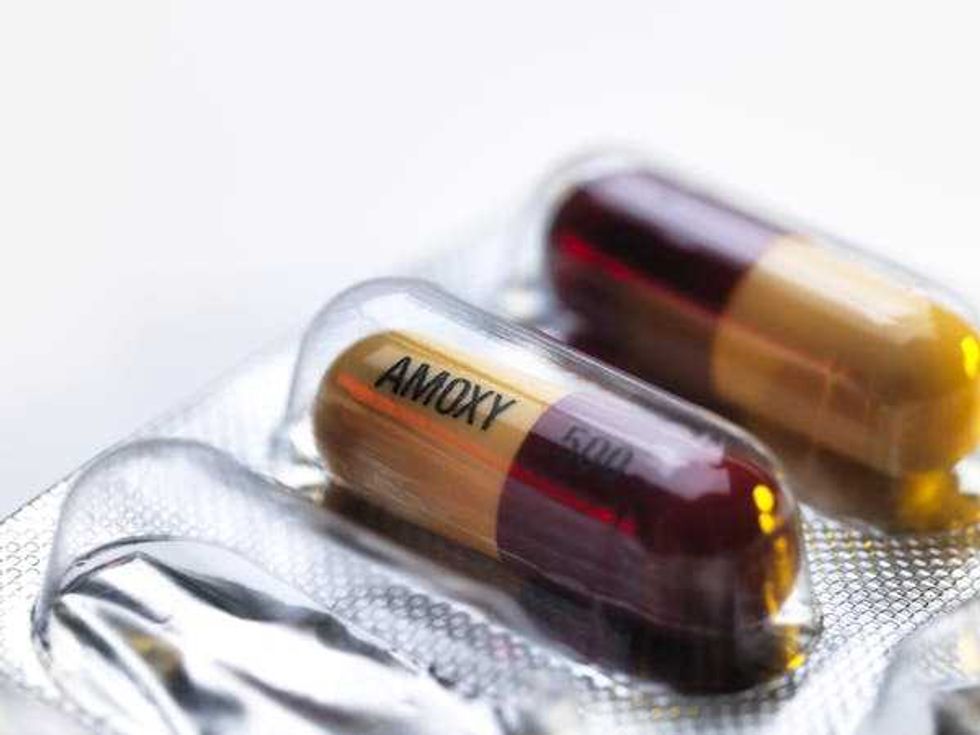 Amoxicillin is a commonly prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Amoxicillin is a commonly prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotic. 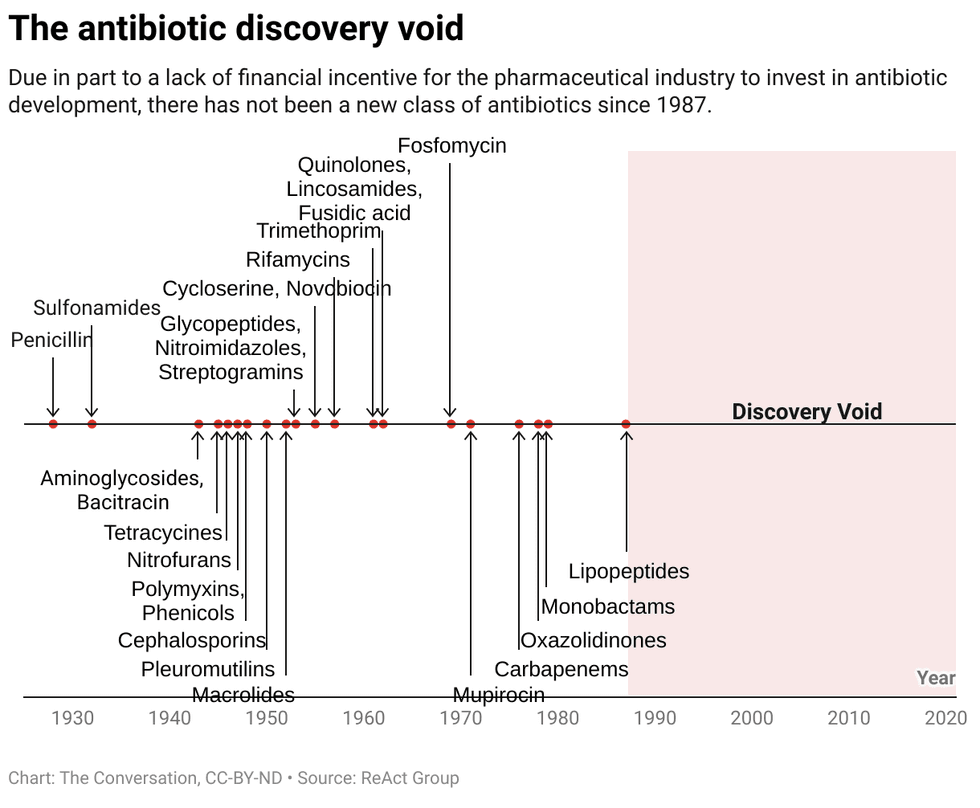 Chart: The Conversation, CC-BY-ND
Chart: The Conversation, CC-BY-ND
 Counterintuitively, social media can make you feel more bored and lonely.
Counterintuitively, social media can make you feel more bored and lonely. Talking about what you’ve read can add a social dimension to what can be a solitary activity.
Talking about what you’ve read can add a social dimension to what can be a solitary activity.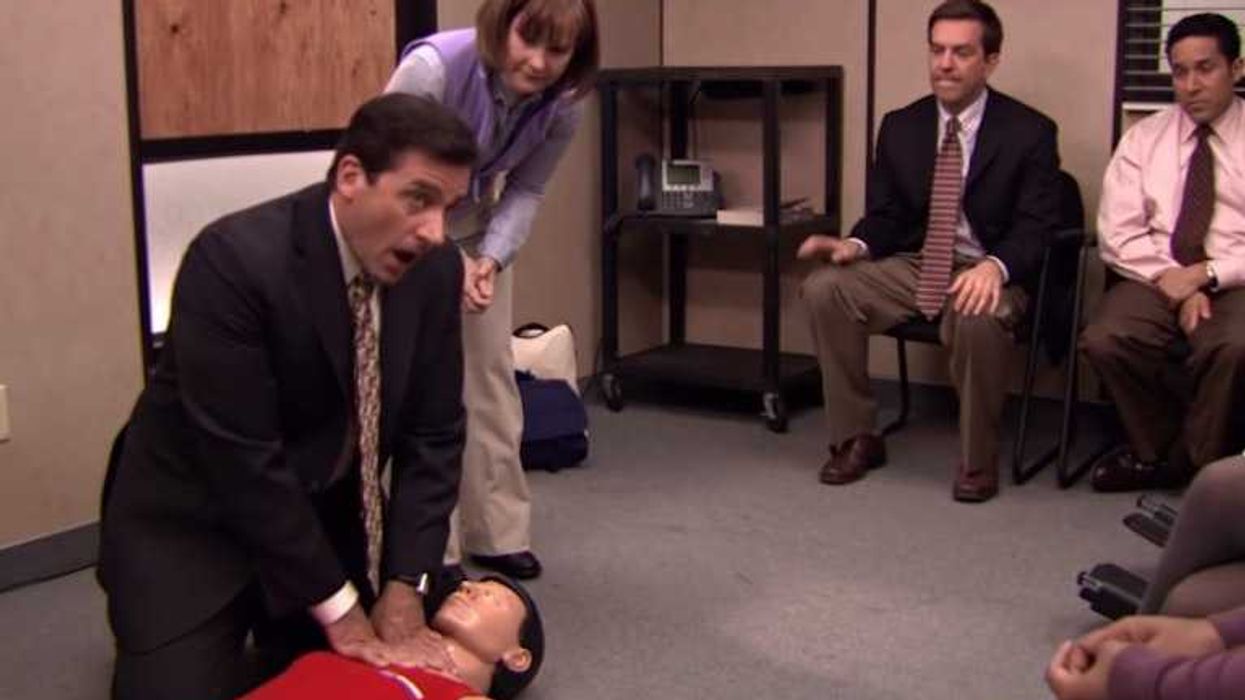 
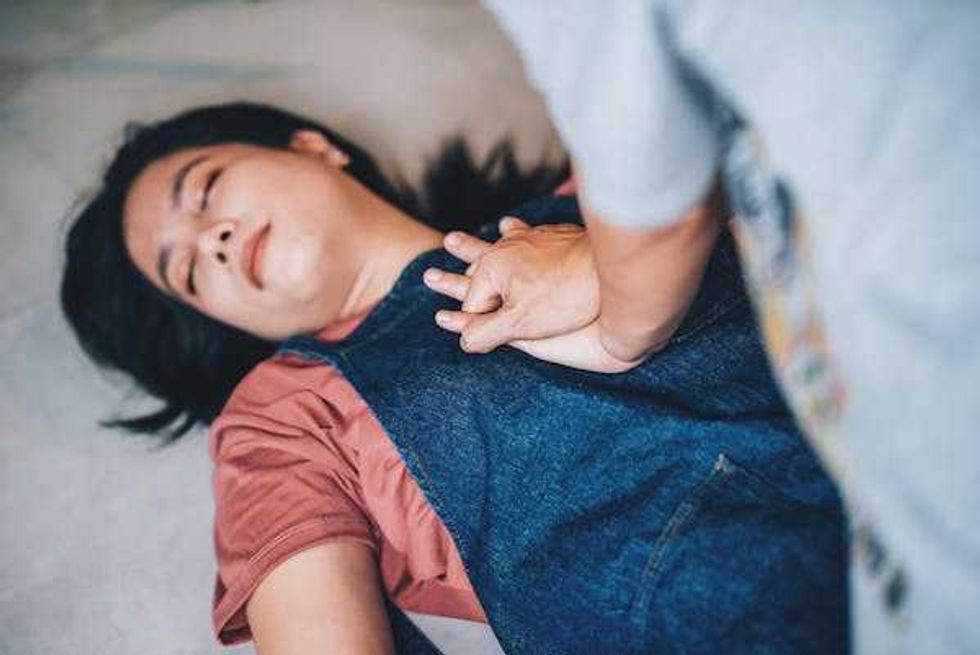 Women and people of color who experience cardiac arrest are less likely to receive CPR.
Women and people of color who experience cardiac arrest are less likely to receive CPR.

 Mushrooms containing psilocybin.Photo credit:
Mushrooms containing psilocybin.Photo credit:  Woman undergoing cancer treatments looks out the window.Photo credit:
Woman undergoing cancer treatments looks out the window.Photo credit:  Friend and patient on a walk.Photo credit:
Friend and patient on a walk.Photo credit: