A nationwide lockdown of four to six weeks would help contain the coronavirus pandemic and need not cause economic hardship, according to Dr. Michael Osterholm, a top health adviser to President-elect Joe Biden, who said that paying people to stay home would limit the spread of Covid-19 in the United States and put the country on track for a smoother recovery.
In an interview with CNBC earlier this week, Osterholm, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota and a member of Biden's coronavirus advisory board, acknowledged that people have clashing interpretations of the meaning and consequences of a "lockdown."
Part of the problem, the epidemiologist explained, is that public health and economic health have been pitted against each other, the implication being that too many people view far-reaching interventions to get the pandemic under control as economically harmful.
"It's a false notion to keep the economy going versus Covid," Osterholm said. "When Covid is running out of control, the economy is going to be suffering mightily. So the things we have to do to get Covid under control will ultimately affect the economy in a positive way."
"Look no further than Asia, which has done a remarkable job of bringing these cases under control, and look what's happening to their economy," he added.
On Wednesday, Osterholm told Yahoo! Finance that "we could pay for a package right now to cover all of the lost wages for individual workers, for losses to small companies, to medium-sized companies or city, state, [and] county governments."
The federal government "could do all of that," he noted, and if it did, "then we could lock down for four to six weeks."
"And if we did that, we could drive the numbers down, like they've done in Asia, like they did in New Zealand and Australia," said Osterholm. "And then, we could really watch ourselves, cruising into the vaccine availability in the first and second quarter of next year, and bringing back the economy long before that."
The alternative—continuing with the inadequate and haphazard measures that characterize the status quo—ensures that the U.S. will remain on a bleak trajectory, public health officials say.
As Common Dreams reported Wednesday, the coronavirus crisis is entering an extremely dangerous phase that has some epidemiologists worried about whether the U.S. has a sufficient number of mobile morgues.
Yet, at precisely the moment when the ongoing catastrophe warrants a stronger, more effective response, President Donald Trump is engaging in what journalist David Dayen on Wednesday called "the world's worst coup attempt."
By hampering Biden's ability to get a head start on facilitating a well-coordinated response to the Covid-19 emergency and its economic fallout, Dayen explained, Trump is relegating even more Americans to "death and suffering."
"The next three to four months are going to be, by far, the darkest of the pandemic," Osterholm told CNBC earlier this week.
"What America has to understand is that we are about to enter Covid hell. It is happening," said Osterholm. "I don't think America quite gets this yet. This is going to get much worse."
"This is not to scare people out of their wits," he added. "It's to scare people into their wits... We can basically limit the contacts we have with people, [which] will dramatically impact our risk of getting this disease."
To save thousands of lives and the economy, however, Osterholm stressed on Wednesday that a comprehensive and stringent lockdown is necessary.
He referred to a New York Times op-ed, co-authored in August with Minneapolis Federal Reserve president Neel Kashkari, in which they argued that the U.S. "reopened too quickly."
"To successfully drive down our case rate to less than one per 100,000 people per day, we should mandate sheltering in place for everyone but the truly essential workers," wrote Osterholm and Kashkari. "We have the resources to support those who have been laid off... Congress should be aggressive in supporting people who've lost jobs because of Covid-19."
"There is no trade-off between health and the economy," they noted. "Both require aggressively getting control of the virus."
"History," Osterholm and Kashkari added, "will judge us harshly if we miss this life- and economy-saving opportunity to get it right this time."
This article first appeared on Common Dreams. You can read it here.















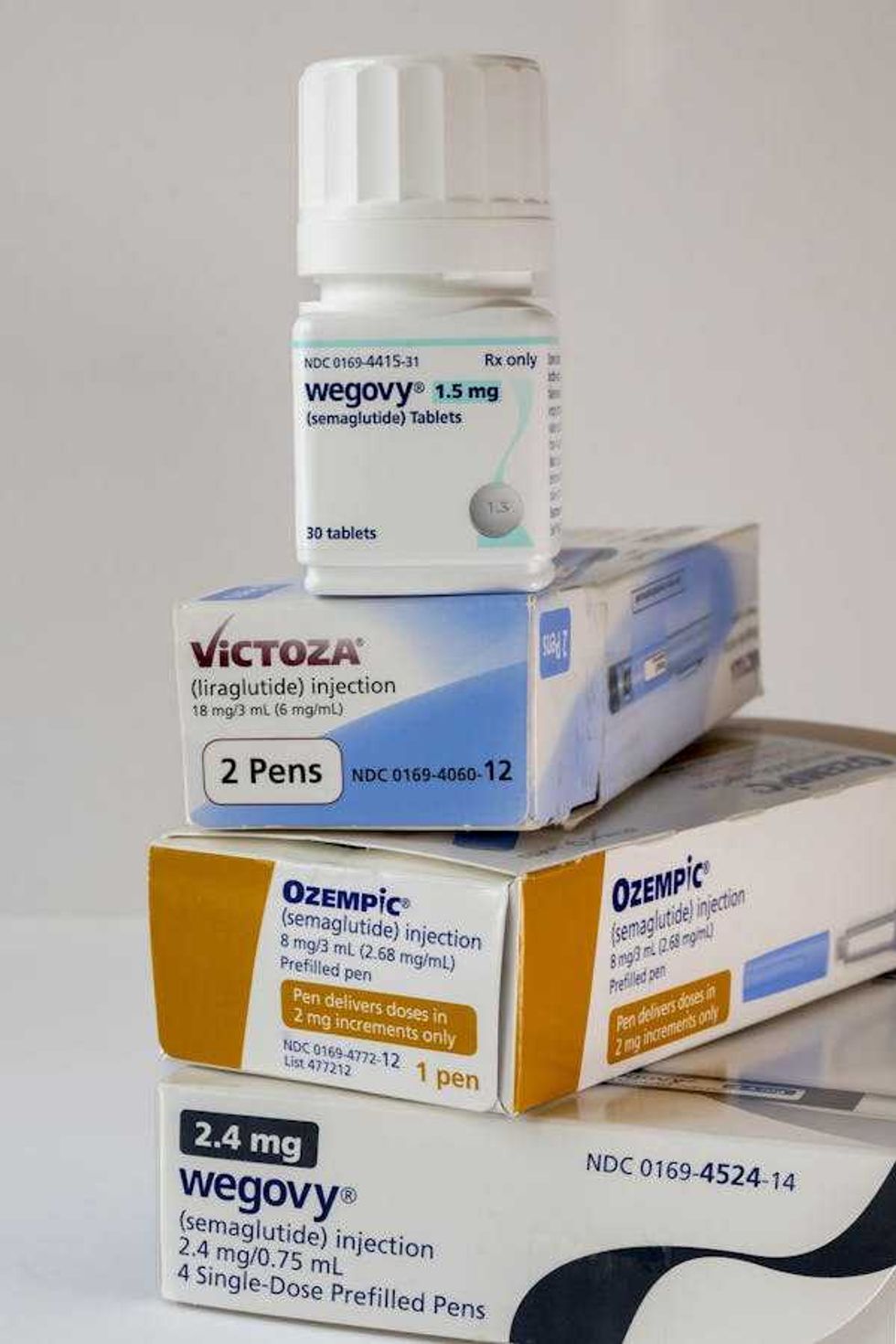 Oral Wegovy pills were approved by the Food and Drug Administration in December 2025 and became available for purchase in the U.S. in January 2026.
Oral Wegovy pills were approved by the Food and Drug Administration in December 2025 and became available for purchase in the U.S. in January 2026. Despite the effectiveness of GLP-1 drugs for weight loss, there is still no replacement for healthy lifestyle patterns, including regular exercise.
Despite the effectiveness of GLP-1 drugs for weight loss, there is still no replacement for healthy lifestyle patterns, including regular exercise.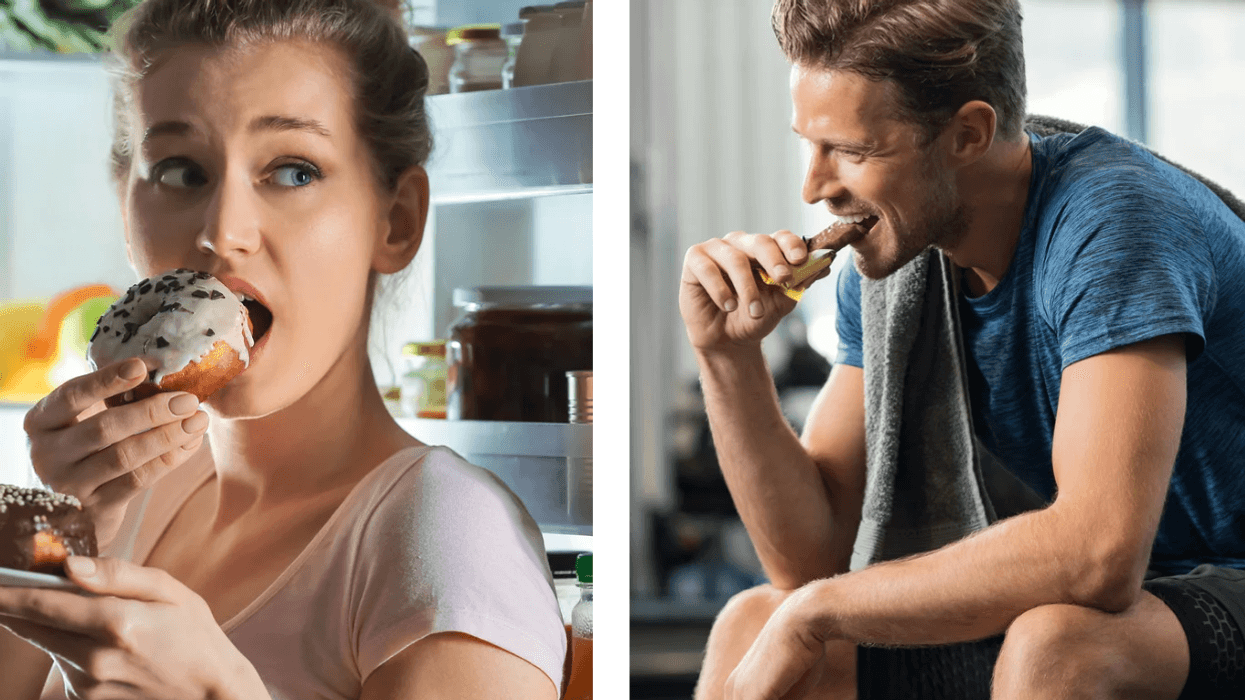

 What foods would you pick without diet culture telling you what to do?
What foods would you pick without diet culture telling you what to do?  Flexibility can help you adapt to – and enjoy – different food situations.
Flexibility can help you adapt to – and enjoy – different food situations.
 Anxious young woman in the rain.Photo credit
Anxious young woman in the rain.Photo credit  Woman takes notes.Photo credit
Woman takes notes.Photo credit 
 Revenge can feel easier than forgiveness, which often brings sadness or anxiety.
Revenge can feel easier than forgiveness, which often brings sadness or anxiety.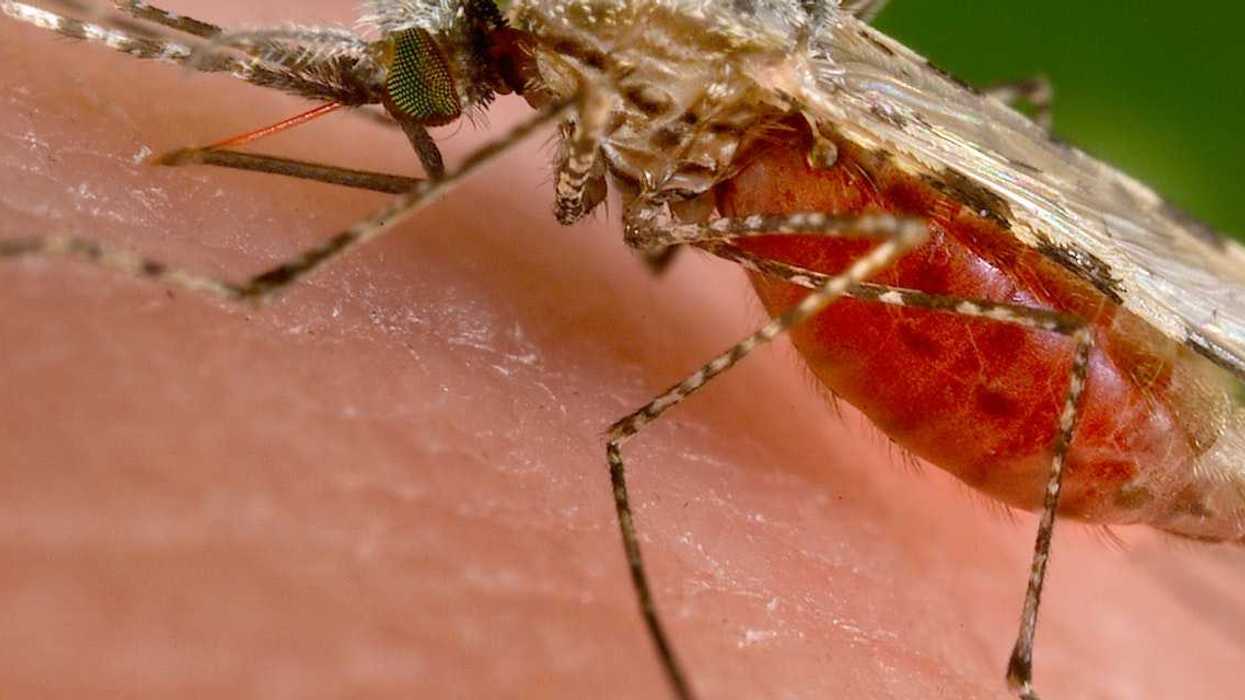 
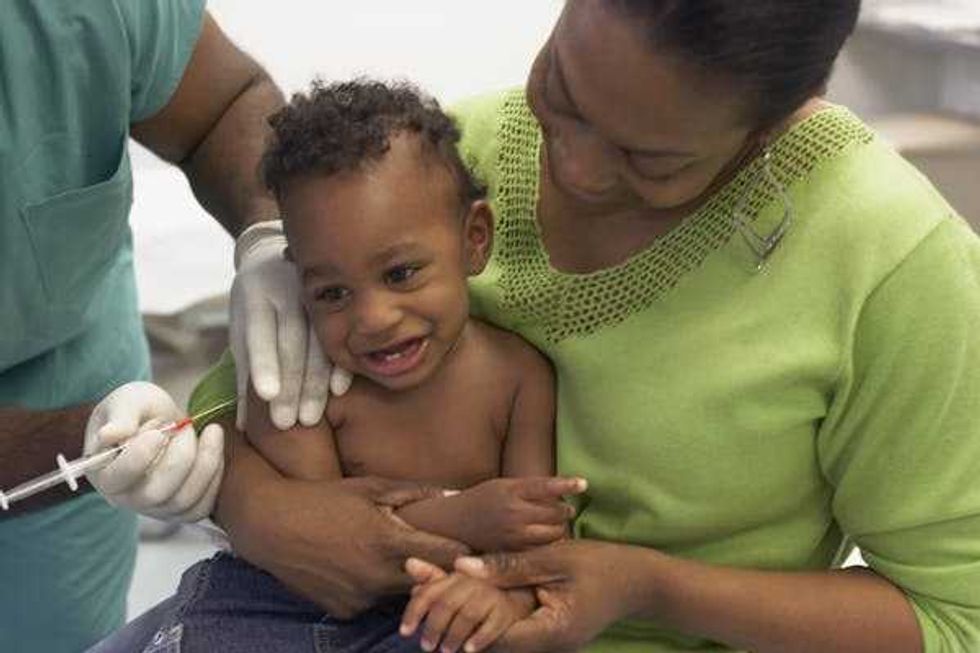 In the past two years, two malaria vaccines have become available for babies starting at 5 months of age.
In the past two years, two malaria vaccines have become available for babies starting at 5 months of age.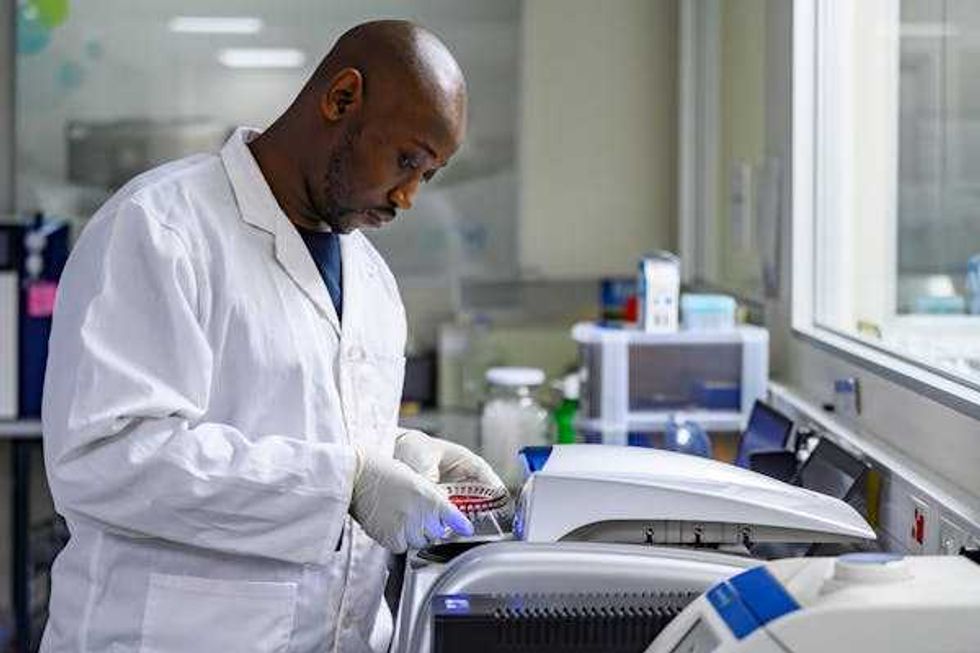 By exploiting vulnerabilities in the malaria parasite’s defense system, researchers hope to develop a treatment that blocks the parasite from entering cells.
By exploiting vulnerabilities in the malaria parasite’s defense system, researchers hope to develop a treatment that blocks the parasite from entering cells.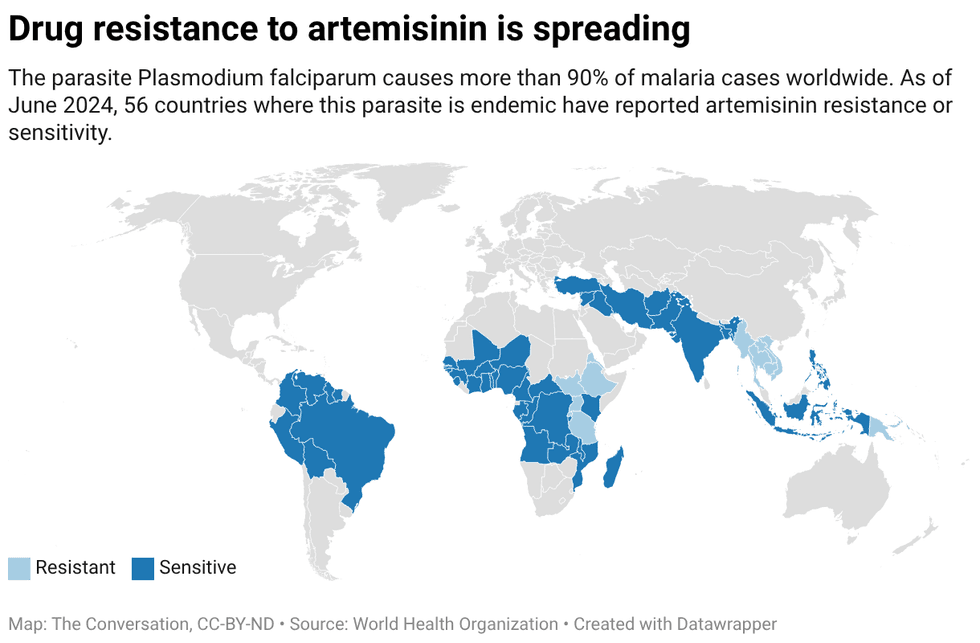 Created with
Created with