There are now two COVID-19 vaccines that, at least according to preliminary reports, appear to be 94.5% and 95% effective. Both were developed in a record-breaking 11 months or so.
I am an infectious diseases specialist and professor at the University of Virginia. I care for patients with COVID-19 and am conducting the local site for a phase 3 clinical trial of Regeneron's antibody cocktail as a tool to prevent household transmission of COVID-19. I'm also conducting research on how dysregulation of the immune system during SARS-CoV-2 infection causes lung damage.
Despite the vaccines' relatively rapid development, the normal safety testing protocols are still in place.
How long does most vaccine development take?
Vaccines typically take at least a decade to develop, test and manufacture. Both the chickenpox vaccine and FluMist, which protects against several strains of the influenza virus, took 28 years to develop. It took 15 years to develop a vaccine for human papilloma virus, which can cause six kinds of cancer.
It also took 15 years to develop a vaccine for rotavirus, which commonly causes severe, watery diarrhea. It took Jonas Salk six years to develop and test the first polio vaccine, starting with the isolation of the virus.
The Pfizer-BioNTech and the Moderna COVID-19 messenger RNA vaccines, by contrast, have been developed in less than a year. That's a game-changer.
How was this vaccine developed so quickly?
The mRNA vaccines produced by Pfizer and Moderna are faster to develop as they do not require companies to produce protein or weakened pathogen for the vaccine.
Traditional vaccines typically use a weakened version of the pathogen or a protein piece of it, but because these are grown in eggs or cells, developing and manufacturing vaccines takes a long time.
By contrast, by using just the genetic material that makes the Spike glycoprotein – the protein on the surface of the coronavirus that is essential for infecting human cells – the design and manufacture of the vaccine is simplified.
The genetic material mRNA is easy to make in a laboratory. Manufacturing an mRNA vaccine rather than a protein vaccine can save months, if not years.
Another factor that accelerated vaccine development was the swift and efficient recruitment of patients for clinical trials.
How is safety assured when vaccine development is so fast?
Safety is the first and foremost goal for a vaccine.
In my opinion, safety is not compromised by the speed of vaccine development and emergency use authorization. The reason that vaccines may be approved so quickly is that the large clinical trials to assess vaccine efficacy and safety are happening at the same time as the large-scale manufacturing preparation, funded by the federal government's Operation Warp Speed program.
Typically, large-scale manufacturing begins only once the vaccine has been tested in clinical trials.
In the case of COVID-19, the U.S. government wanted to be ready to begin distributing the vaccine the moment the results of the phase 3 trials were known and the safety data had been analyzed.
To this end, the pharmaceutical companies launched at-risk manufacturing – which means that the manufactured vaccine doses would be thrown away if the vaccine was ineffective or unsafe – during the FDA-mandated two-month safety waiting period.
The upside is that if the vaccine is safe and effective, it can be distributed immediately, and vaccination can begin.
Are these vaccines riskier than others?
No mRNA vaccines have been approved before because it is relatively new technology.
But these mRNA vaccines appear safe and no riskier than other tried and tested ones, like the childhood measles vaccine. To date, no significant side effects have been reported in the interim phase 3 studies of the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines.
Side effects that have been reported are minor things that one would expect with any vaccine, including soreness at the site of injection and transient fatigue, muscle or joint aches.
How will EUA work?
EUA stands for emergency use authorization.
Under EUA, the FDA is requiring that a COVID-19 vaccine be at least 50% effective at preventing symptomatic illness.
It is also requiring a median of two months of follow-up after completion of the vaccination for half of the vaccine recipients (for most of the vaccines this is two doses). This two-month period is to allow detection of an adverse event from the vaccine.
This article was originally published by The Conversation. You can read it here.













 Volunteers who drive homeless people to shelters talk with a person from Ukraine in Berlin on Jan. 7, 2026.
Volunteers who drive homeless people to shelters talk with a person from Ukraine in Berlin on Jan. 7, 2026.
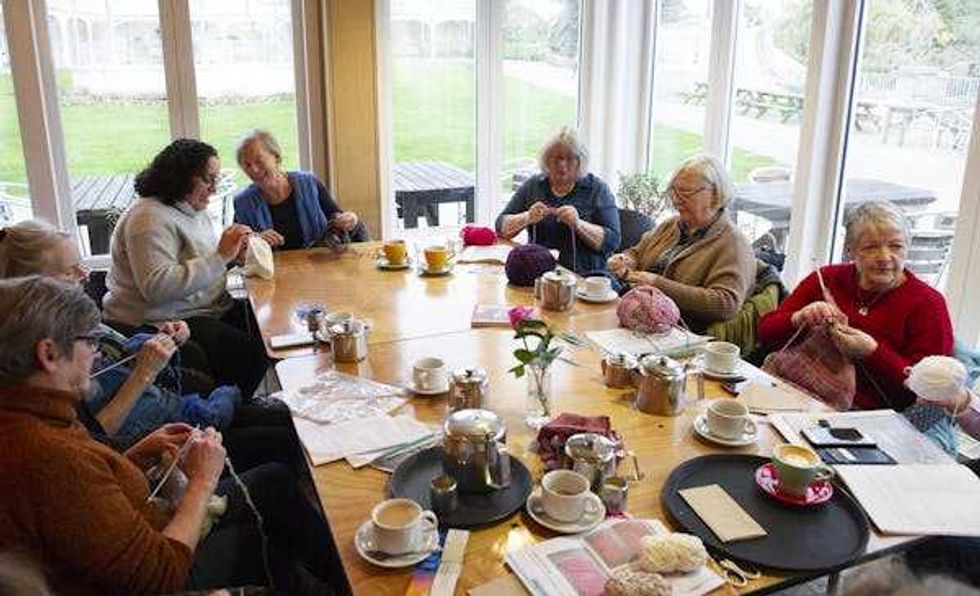 Tasks that stretch your brain just beyond its comfort zone, such as knitting and crocheting, can improve cognitive abilities over your lifespan – and doing them in a group setting brings an additional bonus for overall health.
Tasks that stretch your brain just beyond its comfort zone, such as knitting and crocheting, can improve cognitive abilities over your lifespan – and doing them in a group setting brings an additional bonus for overall health. Overdoing any task, whether it be weight training or sitting at the computer for too long, can overtax the muscles as well as the brain.
Overdoing any task, whether it be weight training or sitting at the computer for too long, can overtax the muscles as well as the brain.
 Amoxicillin is a commonly prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Amoxicillin is a commonly prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotic. 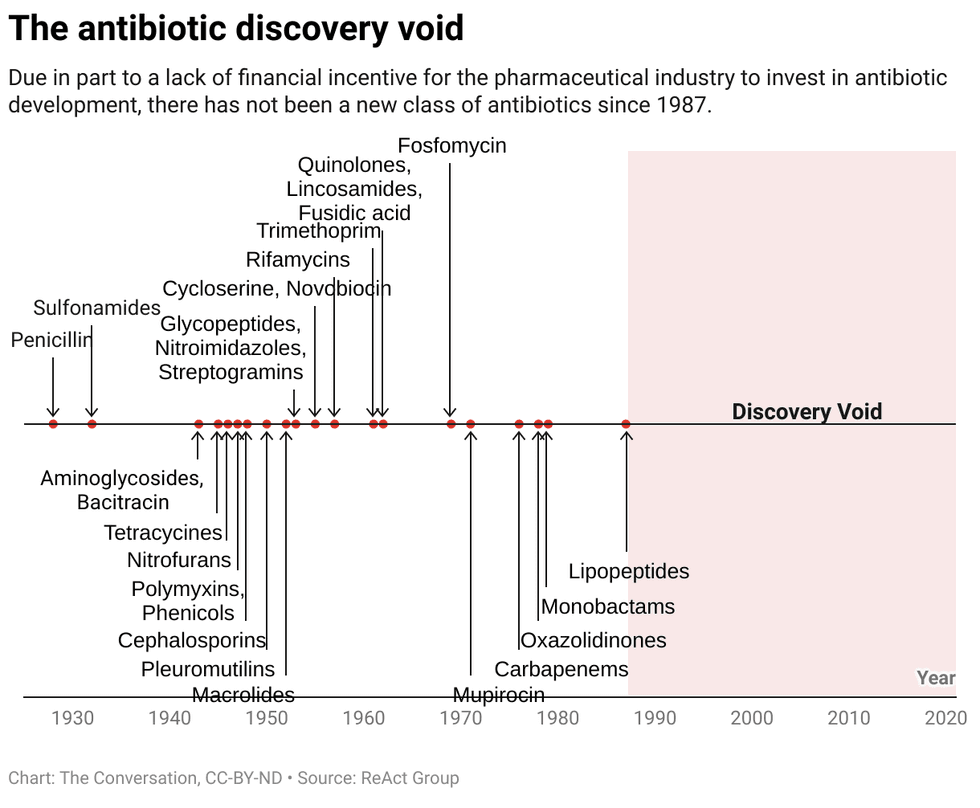 Chart: The Conversation, CC-BY-ND
Chart: The Conversation, CC-BY-ND
 Counterintuitively, social media can make you feel more bored and lonely.
Counterintuitively, social media can make you feel more bored and lonely. Talking about what you’ve read can add a social dimension to what can be a solitary activity.
Talking about what you’ve read can add a social dimension to what can be a solitary activity. 
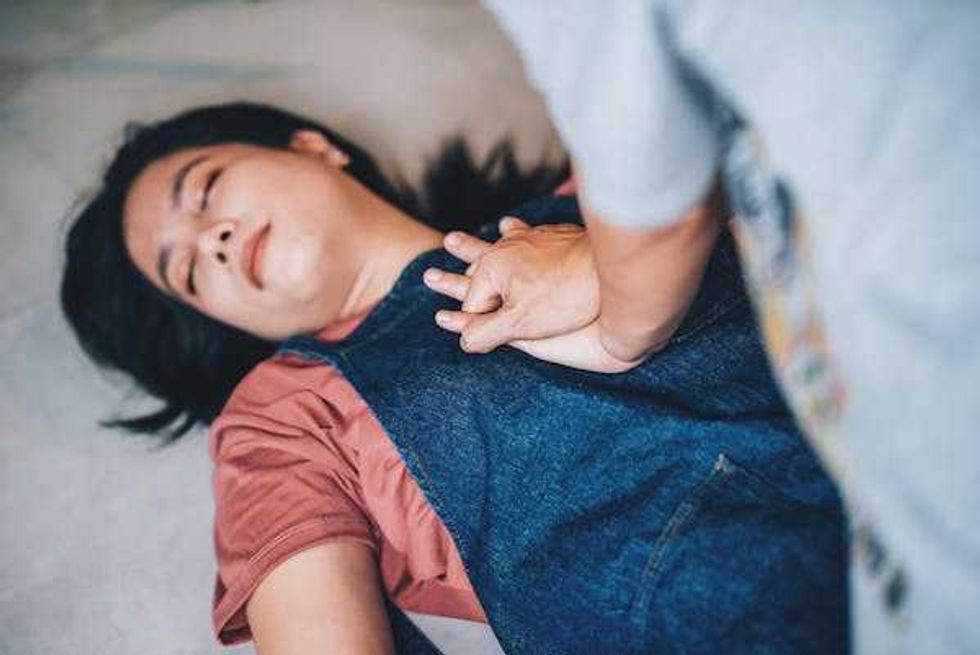 Women and people of color who experience cardiac arrest are less likely to receive CPR.
Women and people of color who experience cardiac arrest are less likely to receive CPR.

 Mushrooms containing psilocybin.Photo credit:
Mushrooms containing psilocybin.Photo credit:  Woman undergoing cancer treatments looks out the window.Photo credit:
Woman undergoing cancer treatments looks out the window.Photo credit:  Friend and patient on a walk.Photo credit:
Friend and patient on a walk.Photo credit: