Do you have anxiety? Have you tried just about everything to get over it, but it just keeps coming back? Perhaps you thought you had got over it, only for the symptoms to return with a vengeance? Whatever your circumstances, science can help you to beat anxiety for good.
Anxiety can present as fear, restlessness, an inability to focus at work or school, finding it hard to fall or stay asleep at night, or getting easily irritated. In social situations, it can make it hard to talk to others; you might feel like you're constantly being judged, or have symptoms such as stuttering, sweating, blushing or an upset stomach.
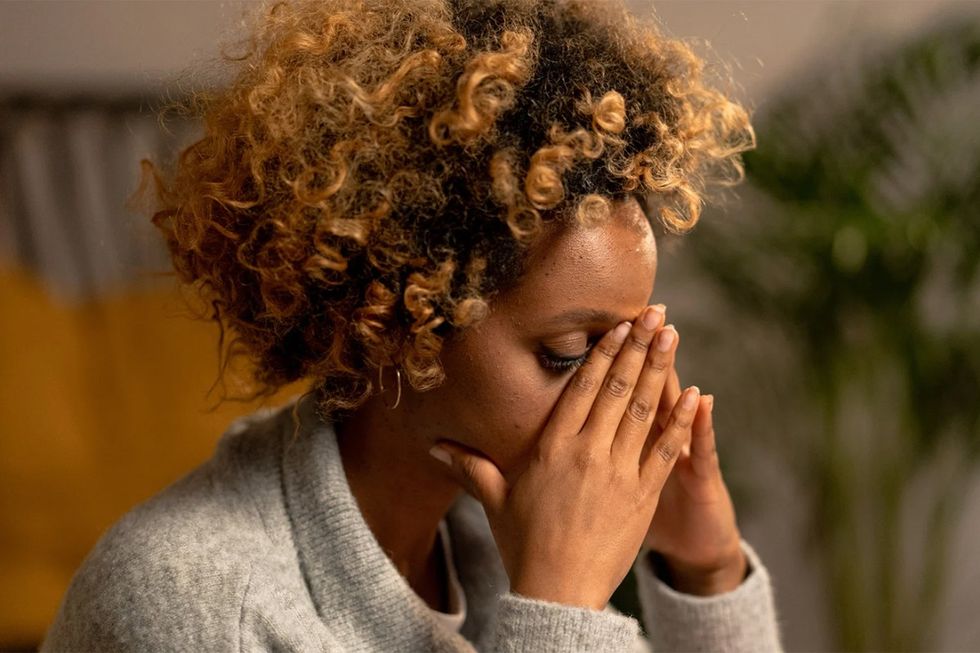

It can appear out of the blue as a panic attack, when sudden spikes of anxiety make you feel like you're about to have a heart attack, go mad or lose control. Or it can be present all the time, as in generalized anxiety disorder, when diffuse and pervasive worry consumes you and you look to the future with dread.
Most people experience it at some point, but if anxiety starts interfering with your life, sleep, ability to form relationships or productivity, you might have an anxiety disorder. Research shows that if left untreated, anxiety can lead to depression, early death and suicide. And while it can indeed lead to such serious health consequences, the medication that is prescribed to treat anxiety doesn't often work in the long-term. Symptoms often return and you're back where you started.
How science can help
The way you handle things in life has a direct impact on how much anxiety you experience. By tweaking your coping strategy you can lower your anxiety levels. Here are some of the top coping skills that have emerged from our study at the University of Cambridge, which will be presented at the 30th European Congress of Neuropsychopharmacology in Paris.
This may sound strange, but the writer and poet GK Chesterton said, "Anything worth doing is worth doing badly." And he has a point. This works so well because it speeds up your decision-making process and catapults you straight into action. Otherwise, you could spend hours deciding how or what you should do, which can be very time-consuming and stressful.
"Anything worth doing is worth doing badly."
— GK Chesterton
People often want to do something "perfectly" or wait for the "perfect time" before starting. However, this can lead to procrastination, long delays, or even prevent us from doing it at all, which causes stress and anxiety.
Instead, why not just start by "doing it badly" and without worrying about how it's going to turn out? This will not only make it much easier to begin, but you'll also find that you're completing tasks much more quickly than before. More often than not, you'll also discover that you're not doing it that badly after all—even if you are, you can always fine-tune it later.
Using "do it badly" as a motto gives you the courage to try new things, adds a little fun to everything, and stops you worrying too much about the outcome. It's about doing it badly today and improving as you go. Ultimately, it's about liberation.
Forgive yourself and 'wait to worry'
Are you particularly critical of yourself and the blunders you make? Well, imagine if you had a friend who constantly pointed out everything that was wrong with you and your life. You'd probably want to get rid of them right away.
But people with anxiety often do this to themselves so frequently that they don't even realize it anymore. They're just not kind to themselves.
So perhaps it's time to change and start forgiving ourselves for the mistakes we make. If you feel like you've embarrassed yourself in a situation, don't criticize yourself – simply realize that you have this impulse to blame yourself, then drop the negative thought and redirect your attention back to the task at hand or whatever you were doing.
Another effective strategy is to "wait to worry." If something went wrong and you feel compelled to worry (because you think you screwed up), don't do this immediately. Instead, postpone your worry – set aside 10 minutes each day during which you can worry about anything.
If you do this, you'll find that when you come back to the situation that triggered the initial anxiety, you won't perceive it as bothersome or worrisome. Our thoughts actually decay very quickly if we don't feed them with energy.
Find purpose in life by helping others
It's also worth considering how much of your day is spent with someone else in mind? If it's very little or none at all, then you're at a high risk of poor mental health. Regardless of how much we work or the amount of money we make, we can't be truly happy until we know that someone else needs us and depends on our productivity or love.
This doesn't mean that we need people's praise, but doing something with someone else in mind takes the spotlight off of us (and our anxieties and worries) and places it onto others – and how we can make a difference to them.
Being connected to people has regularly been shown to be one of the most potent buffers against poor mental health. The neurologist Viktor Frankl wrote:
"For people who think there's nothing to live for, nothing more to expect from life — the question is getting these people to realise that life is still expecting something from them."
"...the question is getting these people to realise that life is still expecting something from them."
— Viktor Frankl
Knowing that someone else needs you makes it easier to endure the toughest times. You'll know the "why" for your existence and will be able to bear almost any "how".
So how can you make yourself important in someone else's life? It could be as simple as taking care of a child or elderly parent, volunteering, or finishing work that might benefit future generations. Even if these people never realize what you've done for them, it doesn't matter because you will know. And this will make you realize the uniqueness and importance of your life.
Olivia Remes is a PhD Candidate at the University of Cambridge.
This article first appeared on The Conversation. You can read it here.
This article originally appeared four years ago.


















 What foods would you pick without diet culture telling you what to do?
What foods would you pick without diet culture telling you what to do?  Flexibility can help you adapt to – and enjoy – different food situations.
Flexibility can help you adapt to – and enjoy – different food situations.
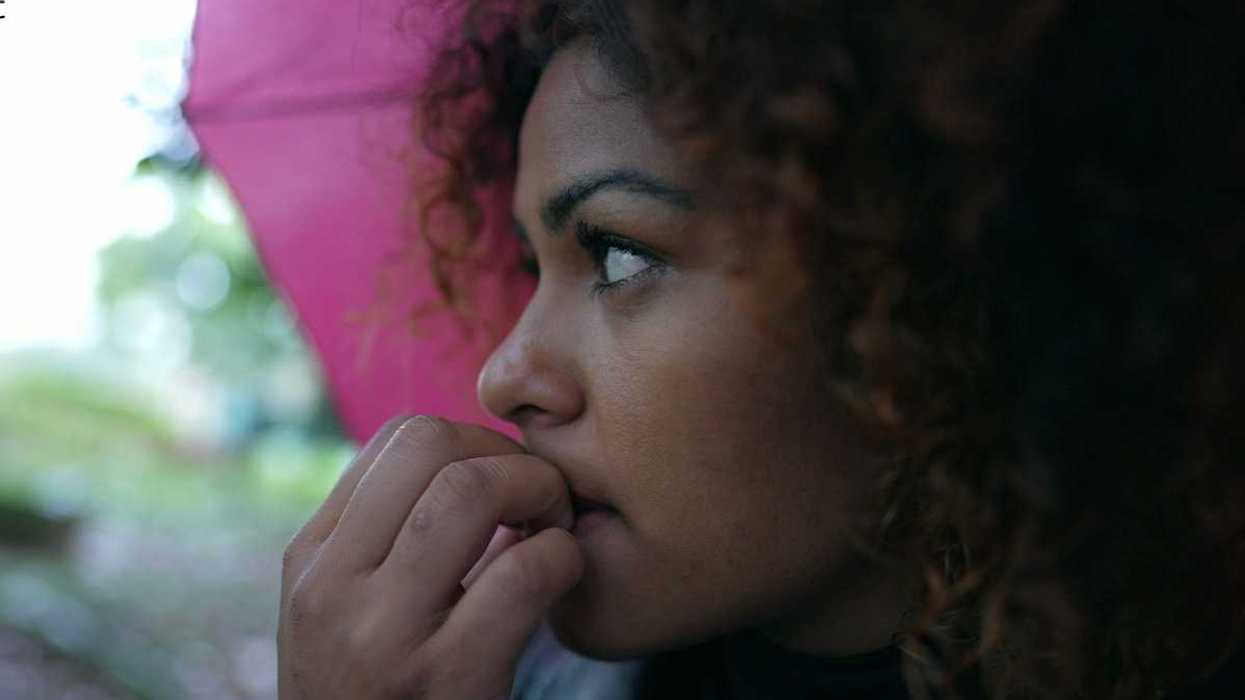 Anxious young woman in the rain.Photo credit
Anxious young woman in the rain.Photo credit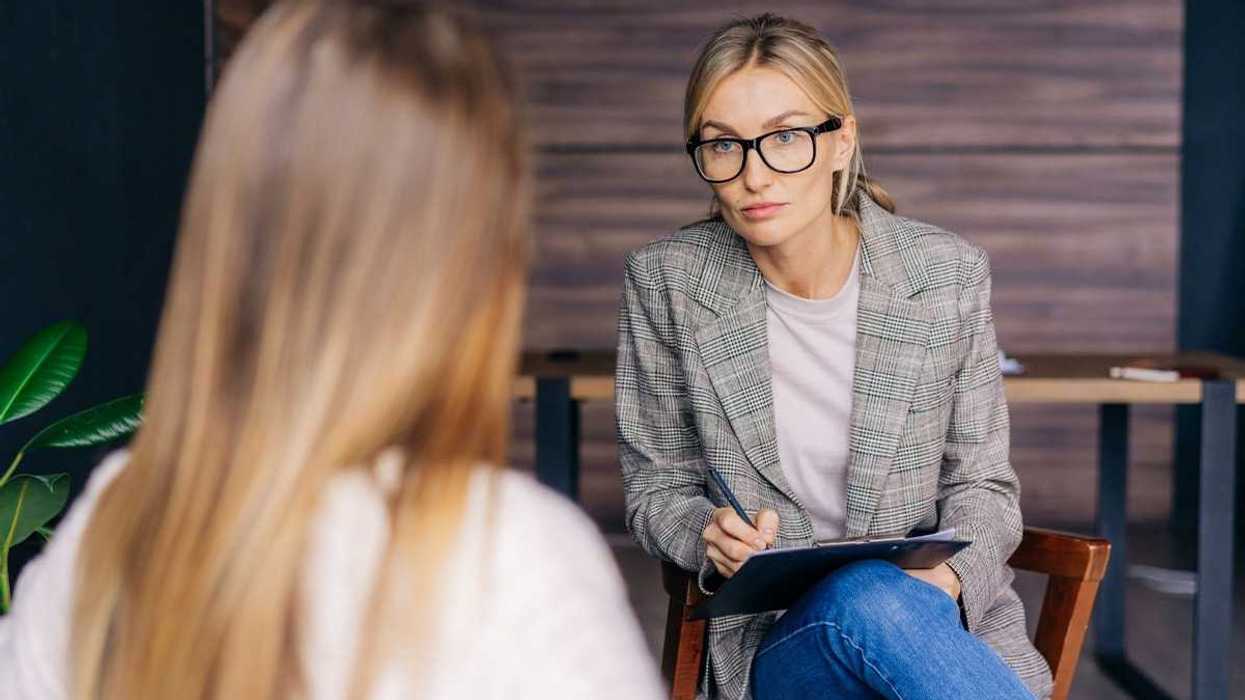  Woman takes notes.Photo credit
Woman takes notes.Photo credit 
 Revenge can feel easier than forgiveness, which often brings sadness or anxiety.
Revenge can feel easier than forgiveness, which often brings sadness or anxiety.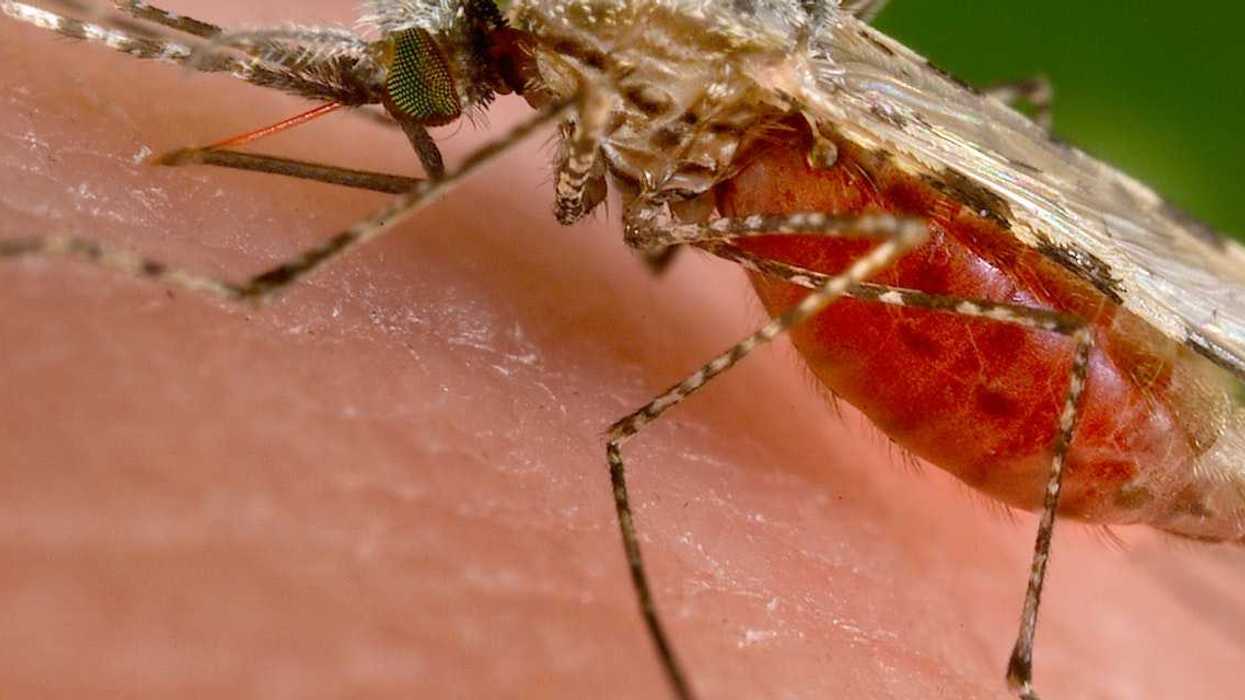 
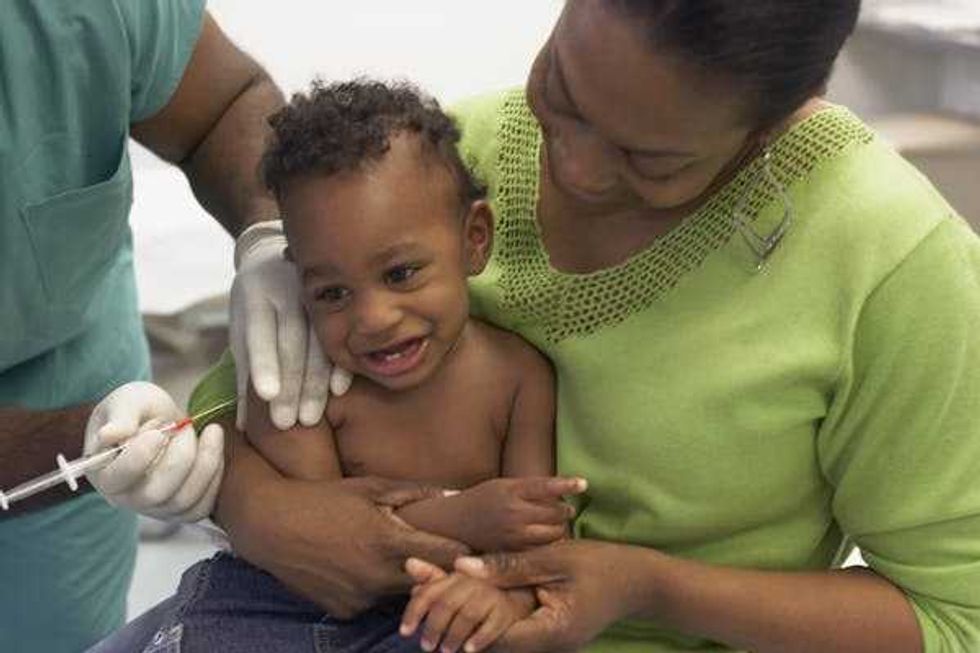 In the past two years, two malaria vaccines have become available for babies starting at 5 months of age.
In the past two years, two malaria vaccines have become available for babies starting at 5 months of age.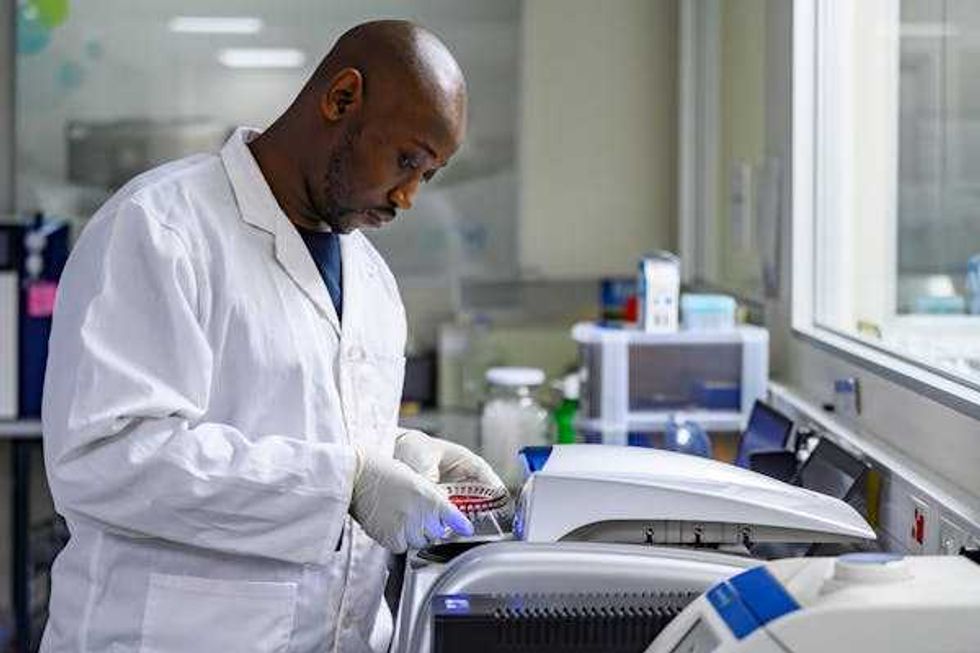 By exploiting vulnerabilities in the malaria parasite’s defense system, researchers hope to develop a treatment that blocks the parasite from entering cells.
By exploiting vulnerabilities in the malaria parasite’s defense system, researchers hope to develop a treatment that blocks the parasite from entering cells.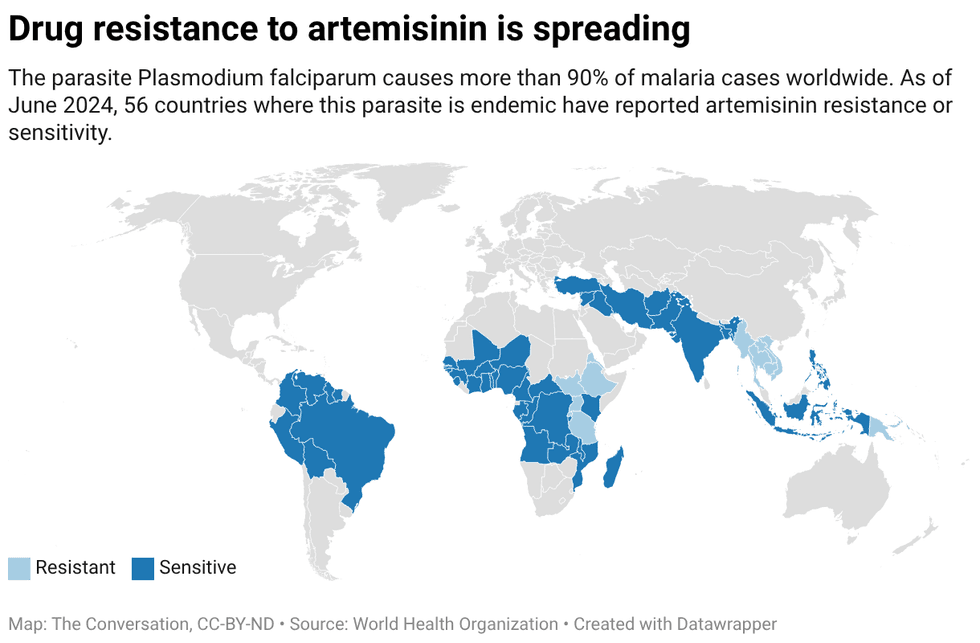 Created with
Created with