The planet Earth keeps time. We all synchronize our clocks to the Earth's rotation. As much as we adjust our calendars with daylight saving or throw in the occasional leap year, it's actually a little more complicated than just that.
The normal day clocks in with about 86,400 seconds. However, since 2020, many days have fallen short of that mark. Even though you haven't felt it, geophysicists have measured the Earth's pulse and discovered it's speeding up. By next summer, expect some record-breaking fast days.
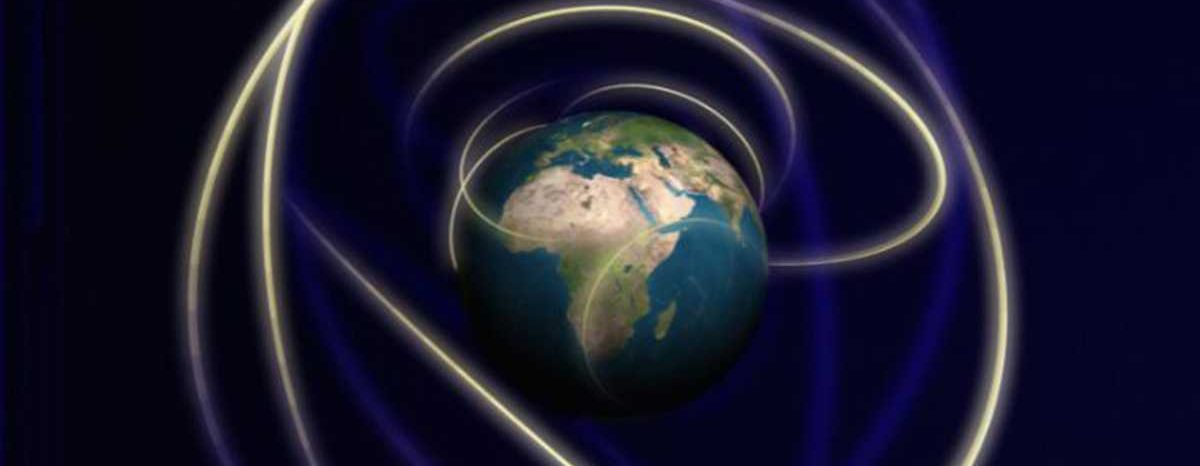

Why is the Earth speeding up?
The primary reason is the gravitational tidal forces exerted by the Moon. The Moon's gravity slowly pulls on the Earth, causing a slight slowing of its rotation. As the tides of the ocean are pulled, it also affects the rotation. A 2022 scientific study in AGU Advancing Earth and Space Sciences found that as the Moon slowly drifts farther away from Earth, the pull weakens, and our planet's rotation increases. Increased planetary rotation means faster spins in front of the Sun; shorter days are here to stay.

How short a day are we talking about?
The world's timekeepers may have to update their clocks, but the necessary adjustment is minimal. In fact, we don't even notice it. Duncan Agnew, a geophysicist at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California, San Diego, described it to the AP in a 2024 article on Earth's rotational spin, in terms of fractions of a second. If the clock were 10:59:59, it would need to be adjusted to 11:00. That extra second adjustment is called a "leap second."
Agnew said, "It’s not a huge change in the Earth’s rotation that’s going to lead to some catastrophe or anything, but it is something notable. It’s yet another indication that we’re in a very unusual time." Agnew continued, "This is an unprecedented situation and a big deal."

What does that mean for us?
Watch this cool video that has over 10 million views by Neil deGrasse Tyson talking about the Earth's rotation dramatically changing here:
- YouTube www.youtube.com
The Earth is a giant cosmic clock that shapes the length of our days and the rhythm of our bodies. As the spin of the world subtly shifts a few milliseconds, don't be surprised if your mood slowly changes. We are connected to more than just our communities. We are connected to the rhythms of the planet.















 Left: A robotic arm. Right: Rice grains.Photo credit:
Left: A robotic arm. Right: Rice grains.Photo credit: 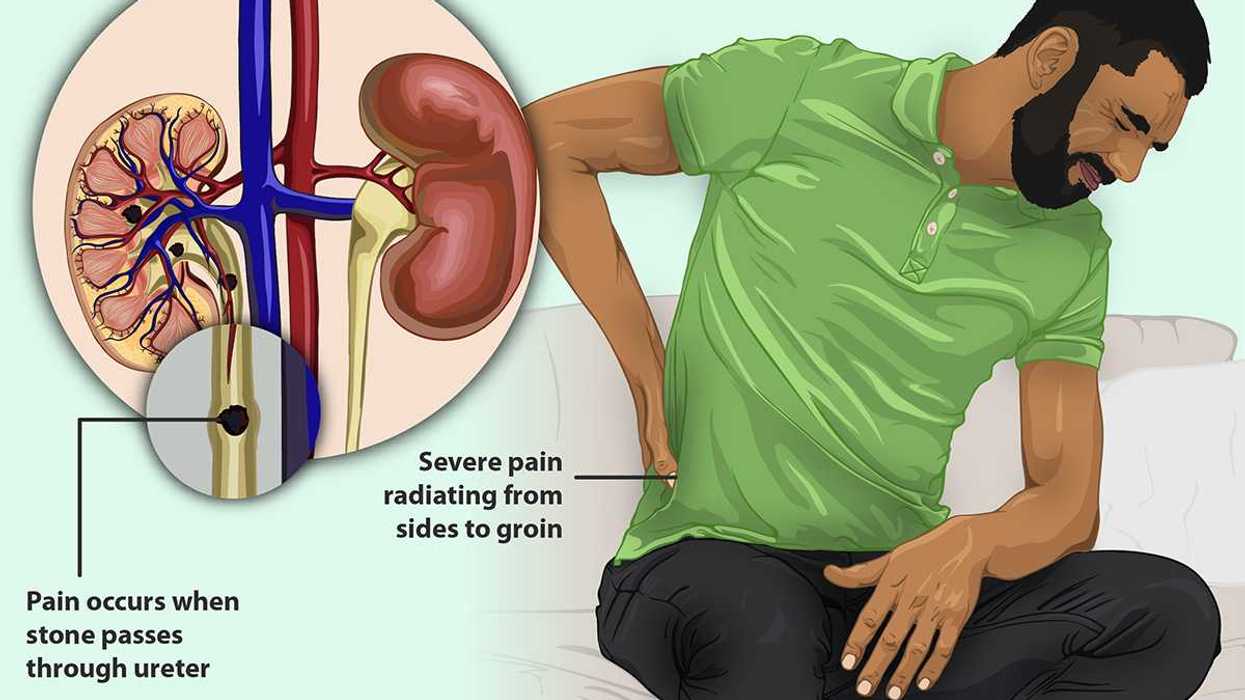 A diagram on kidney stones.myupchar/
A diagram on kidney stones.myupchar/ 
 Christy Lam-Julian, a mother in Pinole, Calif., reads to her son in April 2025.
Christy Lam-Julian, a mother in Pinole, Calif., reads to her son in April 2025. Children who read bedtime stories with their parents are likely to benefit from a boost in creativity – especially if they consider questions about the books.
Children who read bedtime stories with their parents are likely to benefit from a boost in creativity – especially if they consider questions about the books.