The big idea
Mothers who showed the most academic promise in high school have the same leadership opportunities as fathers who performed the worst, according to
our new peer-reviewed study. That is, in their early-to-mid careers, mothers who got straight A's end up overseeing a similar number of employees as men who got F's.
To reach these conclusions, we used a
U.S. national survey that since 1979 has tracked a group of baby boomers born from 1957 through 1964. We focused on the 5,000 or so participants for whom researchers obtained high school transcripts and then compared the data with their responses to career-focused surveys taken over an 11-year period from 1988 to 1998 – a period when most of them were in their 30s.
Overall, our results showed that men manage more employees than women regardless of their GPA. For participants without children, the leadership gap between men and women was fairly constant across GPA levels, with men managing about two to three workers more on average.
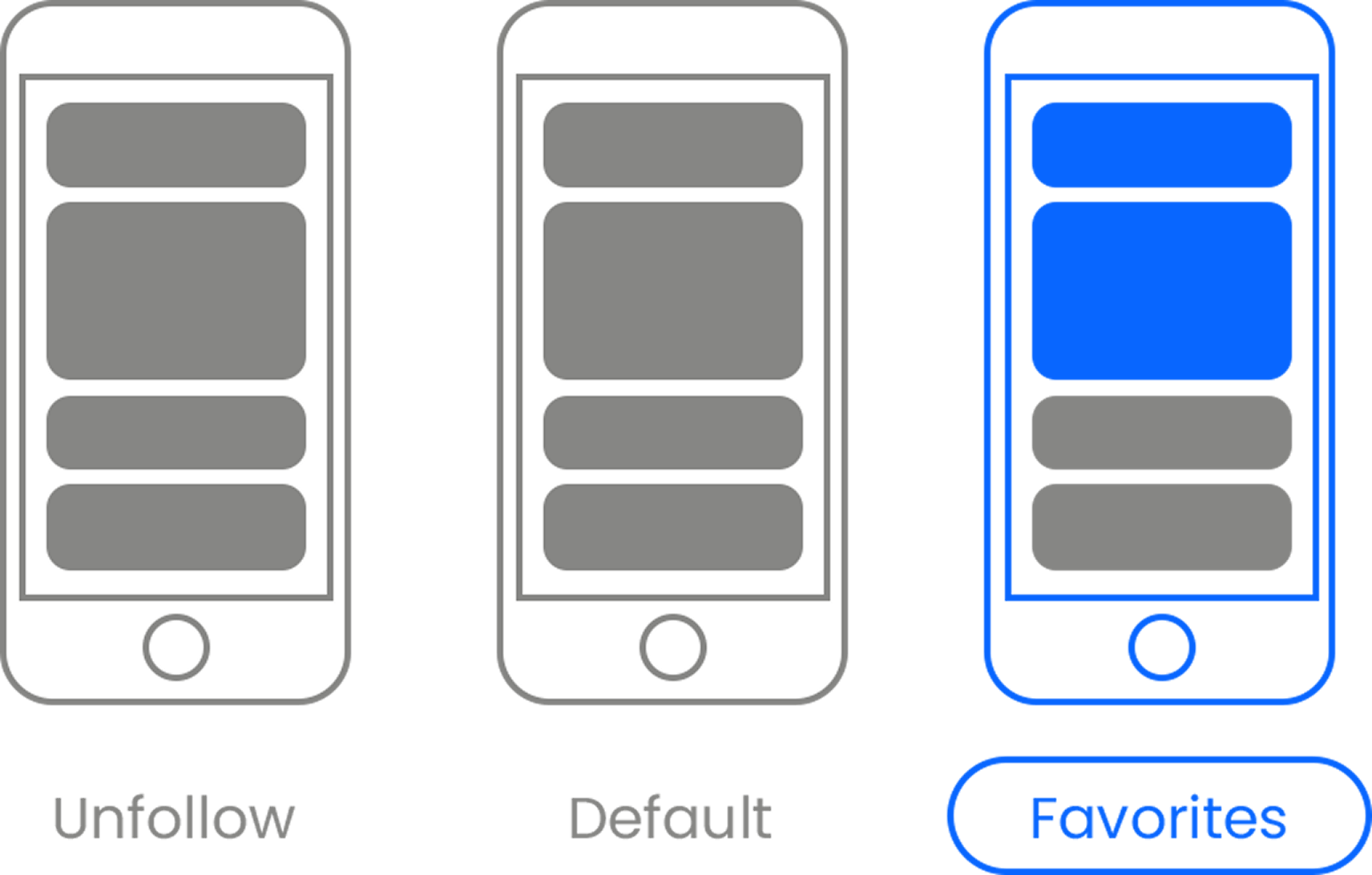
What was most interesting to us is what we learned when we focused only on parents. Fathers with 4.0 GPAs reported overseeing an average of 19 people, compared with 10 for childless men with similar grades and about five for fathers with a 1.0 or less. In contrast, the best-performing mothers managed fewer than five people, compared with seven for childless women with top GPAs and three for mothers with the worst grades.
The motherhood penalty
Mothers with the best grades in high school manage the same number of employees in their early-to-mid careers as men with failing grades. The chart shows the average number of employees each demographic reported overseeing in their late 20s and 30s based on their actual grades in high school.
In other words, becoming a parent boosts leadership opportunities for men while diminishing them for women. Even attaining a college or advanced degree had the same effect, helping fathers but doing little for mothers. Other research reveals that men have a faster route to leadership positions across occupations, including in
stereotypically feminine fields such as human resources and health care.
Why it matters
Recent
economics research has highlighted "lost Einsteins" – the really smart students from poor families who never become inventors because they don't receive the same advantages and support that even low-achieving kids from rich families do.
The same can be said for women, whose talents
have long been underutilized by corporate America. Our research showed that even the most talented and brightest women experience diminished leadership prospects on account of gender-related barriers, especially if they became mothers.
But the problem isn't motherhood or fatherhood per se.
Past research has shown it's more about how society views mothers and fathers and the associated stereotypes that contribute to gendered outcomes. For example, fathers could be getting more leadership opportunities because employers stereotype them as better fits for positions that emphasize authority, long work hours and travel. Mothers, on the other hand, may see fewer chances because employers falsely believe they are less committed or competent.
Employers could help overcome this problem by reviewing how they evaluate workers and adopting fairer promotion practices that
are more likely to recognize women's talent. More family-friendly policies such as paid leave and subsidized child care could also help.
What still isn't known
Given the limits of our sample, we do not know how our findings translate to younger groups, such as millennials. But given that progress toward equality in the workplace has
slowed or even stalled on certain measures in recent decades, we believe it's likely that the leadership prospects of academically gifted women haven't improved much.
What's next
COVID-19
has harmed women's employment and productivity more than men's, particularly among parents because of a lack of child care support. We plan to conduct additional research to better understand how women's leadership opportunities may have been affected by the pandemic.
Jill Yavorsky is an Assistant Professor of Sociology at the University of North Carolina – Charlotte
Yue Qian is an Assistant Professor of Sociology a the University of British Columbia
This article first appeared on The Conversation. You can read it here.















 Tow truck towing a car in its bedCanva
Tow truck towing a car in its bedCanva  Sad woman looks at her phoneCanva
Sad woman looks at her phoneCanva  A group of young people at a house partyCanva
A group of young people at a house partyCanva  Fed-up woman gif
Fed-up woman gif Police show up at a house party
Police show up at a house party 
 A trendy restaurant in the middle of the dayCanva
A trendy restaurant in the middle of the dayCanva A reserved table at a restaurantCanva
A reserved table at a restaurantCanva Gif of Tim Robinson asking "What?' via
Gif of Tim Robinson asking "What?' via 
 An octopus floating in the oceanCanva
An octopus floating in the oceanCanva

 A woman relaxes with a book at homeCanva
A woman relaxes with a book at homeCanva An eviction notice is being attached to a doorCanva
An eviction notice is being attached to a doorCanva Gif of Kristen Bell saying 'Ya basic!' via
Gif of Kristen Bell saying 'Ya basic!' via