This article was originally published on ProPublica. You can read it here.
Nursing home residents have been among those hardest hit by the new coronavirus. In some states, more than half of the recorded deaths have been long-term care residents. Some of the homes have been cited for putting residents at "immediate jeopardy" of harm or death, our analysis showed.
And many of the affected homes have been previously written up for violating federal standards. That's true in California, New Jersey and New York.
We're updating Nursing Home Inspect to include more information about nursing homes across the country, including past problems with infection control practices, and which ones have had cases of COVID-19 among residents or staff.
We introduced this resource in 2012 as a way to search through tens of thousands of nursing home inspection reports to find problems and trends.
You can easily compare the nursing homes in your state based on how many times they have been cited for violating infection control protocols in the past three inspection cycles (roughly three years). We've also added data from The Washington Post on homes with COVID-19 cases. Nursing Home Inspect also allows you to sort by the number of health deficiencies cited by regulators; the number of serious deficiencies per home (that is, deficiencies in which patients were put in immediate jeopardy of harm); the amount of fines imposed; and how often the government has suspended payments to the home for new patients, another type of penalty.
Our data is from the U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), which has its own website called Nursing Home Compare. We've taken the information and organized it into an easy-to-use resource for families and residents, as well as researchers and other journalists.
Our site includes:
• State pages: Every state has its own section that allows you to compare all of the homes in a state on a variety of indicators.
• Individual nursing home pages: Every home has a section listing all of the health deficiencies identified within the past three survey cycles (roughly three years). The full text of these deficiency reports, if available, can be accessed via links from this page to CMS. Each home's page also has ownership status — whether for-profit, government-run or nonprofit — and whether the home has been labeled by the government as a Special Focus Facility, meaning that it has many more problems than other homes. We've also labeled Special Focus Facility candidates, which meet the criteria to be a special focus facility but haven't yet been designated as one. (We only include health deficiencies, not fire and safety violations, in this database.)
• State-by-state maps: The main page of the app shows how states compare in terms of the percentage of homes with at least one serious deficiency, the average fine paid by homes in the state, and the percentage of homes in each state with at least one infection-related deficiency.
• Top 20 Lists: We've listed the homes that have paid the most in fines in the nation and those with the highest number of serious deficiencies.
If homes violate federal standards, CMS may impose fines or suspend Medicare/Medicaid payments to the nursing home for new residents until the facility corrects the deficiency.
If problems persist or are not fixed, CMS can end its agreement with the nursing home. Additional details about CMS' approach to enforcement can be found here.
Nursing Home Inspect continues to allow you to search through nearly 80,000 inspection reports by keywords, such as "choke" or "maggots," to look for issues you care about. These search results can be sorted by date, city, state or severity of the deficiency.
Nursing homes are inspected on both a regular schedule and when there is a complaint. Inspectors typically work for state agencies paid by Medicare. If they find problems, known as deficiencies, they rank them on a scale of A to L, the most severe. The vast majority are either labeled D or E.
What you won't find on these pages are self-reported quality measures for each home. Those can be found on Nursing Home Compare. We also don't list the state sanctions imposed against homes because those are not centrally collected. For information on penalties within a given state, you should consult the state agency that regulates nursing homes. The federal government has a list of contacts available here.
When reading through inspection reports, it is a good idea to keep in mind the caveats we've outlined previously.
How We Combined Data Sources
To compile our app, we used different datasets: a listing of all Medicare-certified nursing homes, inspection violations and penalties, and deficiency report narratives.
We merged spreadsheets containing findings from routine inspections and those identified during complaint visits and kept only health violations, not fire safety violations.
We used each home's unique identification code to match penalties imposed to the dates of their corresponding inspections so we could display that data together for each home. (We also noted some cases in which a penalty date did not have a corresponding inspection in the database.)
You can find the data we used on these sites:
• For a list of nursing homes: https://data.medicare.gov/Nursing-Home-Compare/Provider-Info/4pq5-n9py
• For penalties: https://data.medicare.gov/Nursing-Home-Compare/Penalties/g6vv-u9sr
• For health deficiency information: https://data.medicare.gov/Nursing-Home-Compare/Health-Deficiencies/r5ix-sfxw
• For deficiency report narratives (updated in April 2020): https://downloads.cms.gov/files/Full-Statement-of-Deficiencies-April-2020.zip














 What foods would you pick without diet culture telling you what to do?
What foods would you pick without diet culture telling you what to do?  Flexibility can help you adapt to – and enjoy – different food situations.
Flexibility can help you adapt to – and enjoy – different food situations.
 Anxious young woman in the rain.Photo credit
Anxious young woman in the rain.Photo credit  Woman takes notes.Photo credit
Woman takes notes.Photo credit 
 Revenge can feel easier than forgiveness, which often brings sadness or anxiety.
Revenge can feel easier than forgiveness, which often brings sadness or anxiety.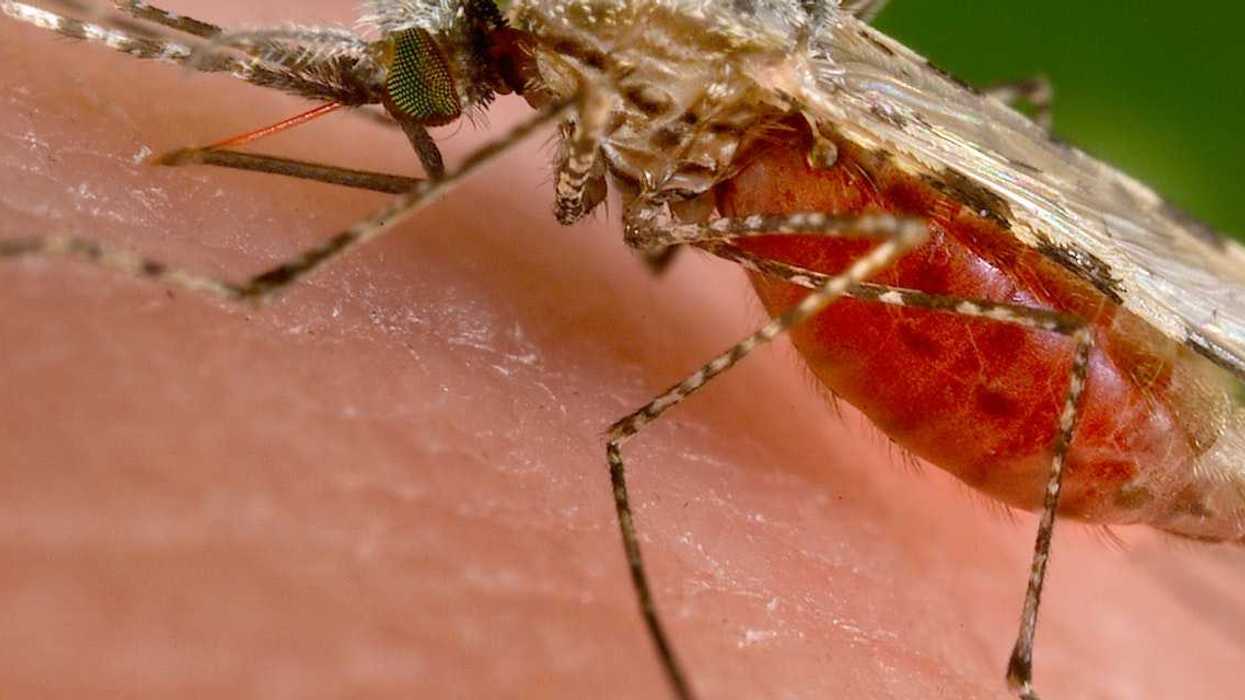 
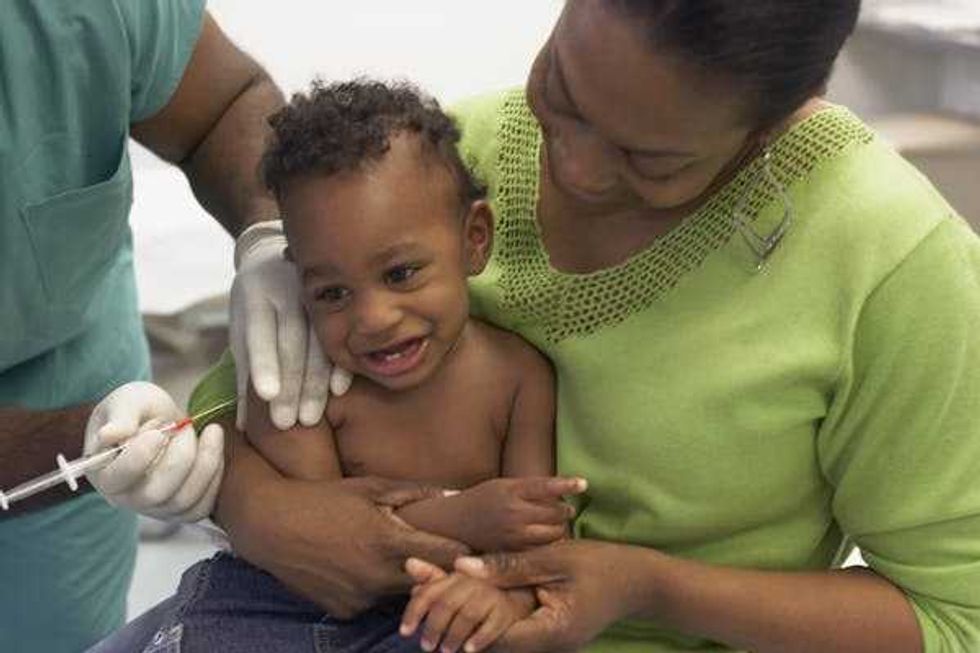 In the past two years, two malaria vaccines have become available for babies starting at 5 months of age.
In the past two years, two malaria vaccines have become available for babies starting at 5 months of age.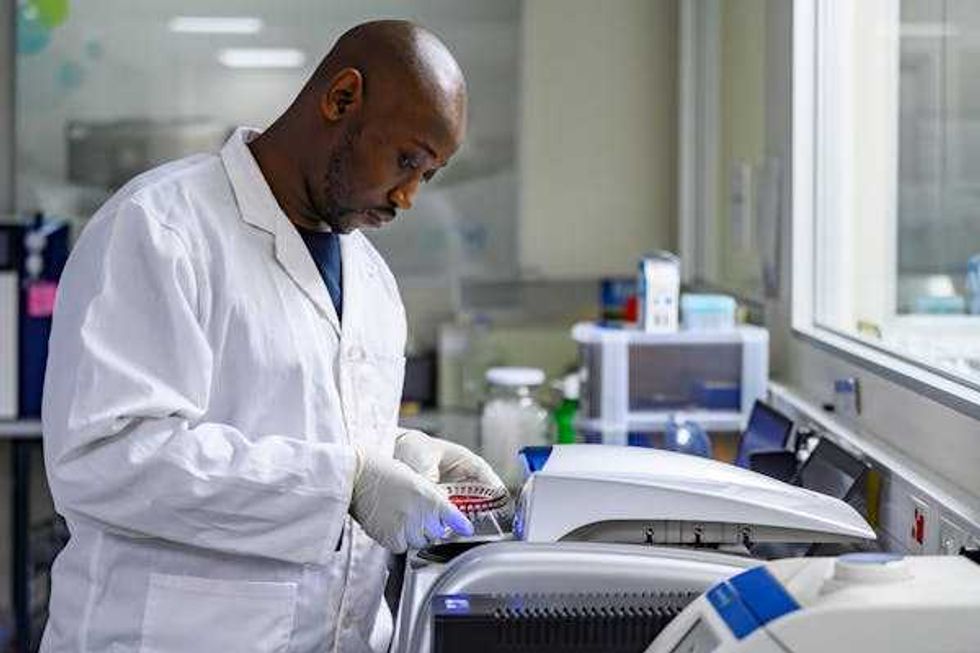 By exploiting vulnerabilities in the malaria parasite’s defense system, researchers hope to develop a treatment that blocks the parasite from entering cells.
By exploiting vulnerabilities in the malaria parasite’s defense system, researchers hope to develop a treatment that blocks the parasite from entering cells.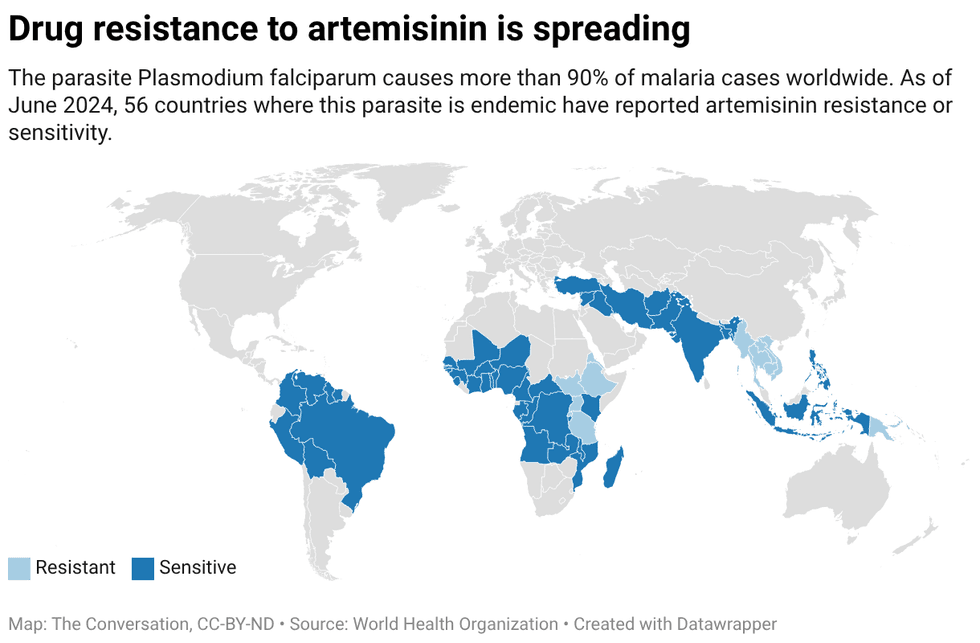 Created with
Created with 
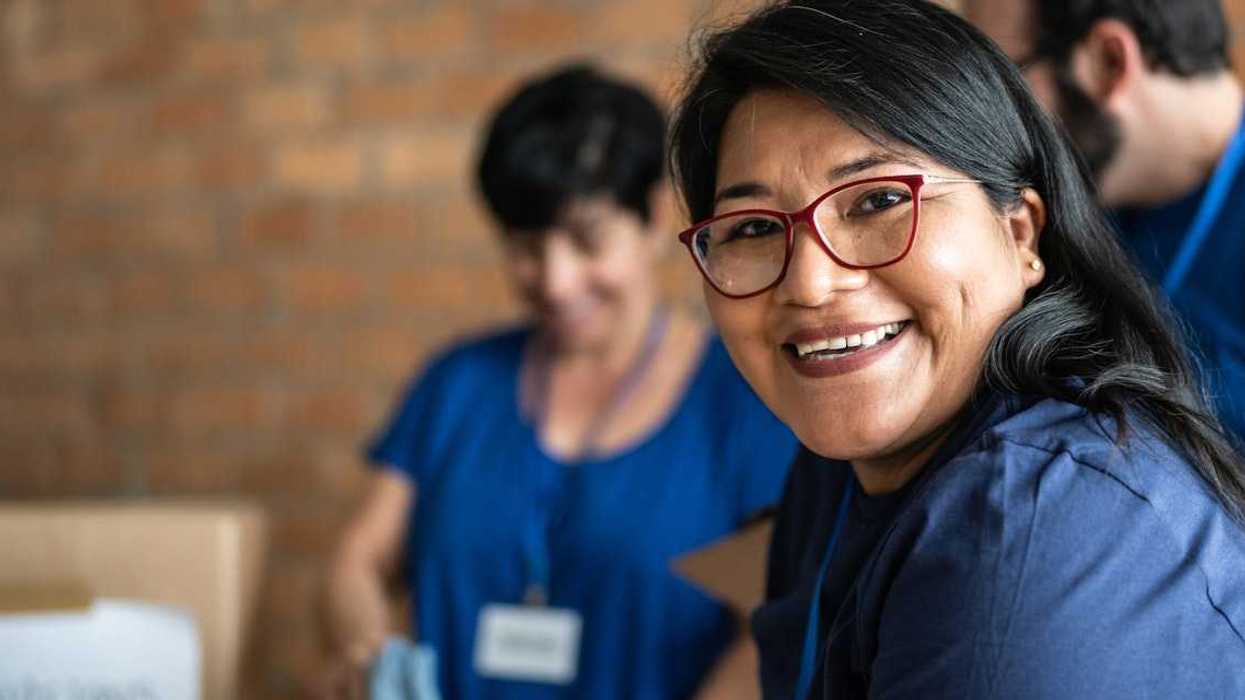
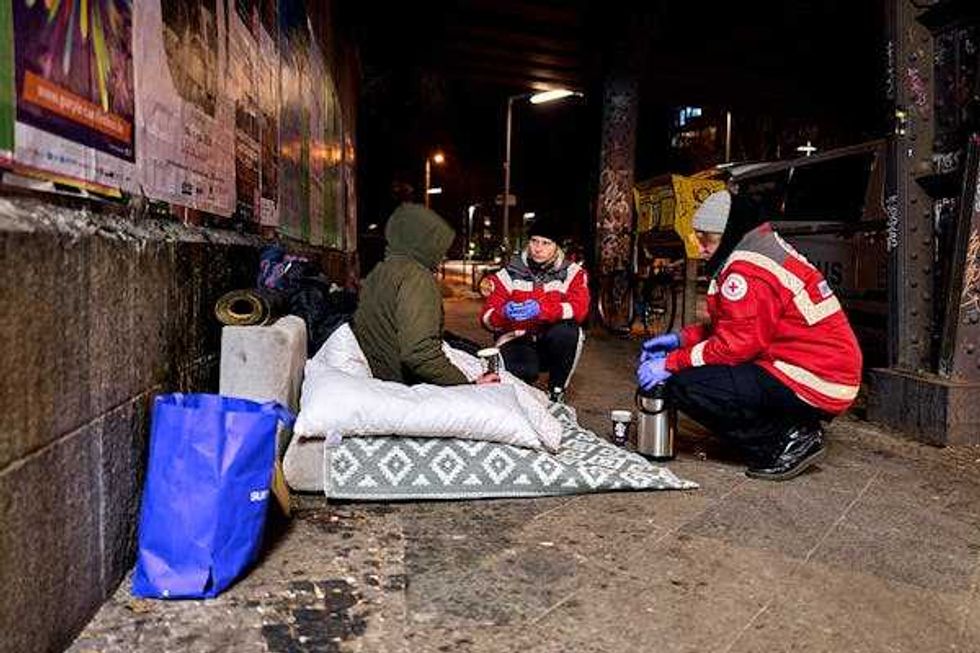
 Volunteers who drive homeless people to shelters talk with a person from Ukraine in Berlin on Jan. 7, 2026.
Volunteers who drive homeless people to shelters talk with a person from Ukraine in Berlin on Jan. 7, 2026.
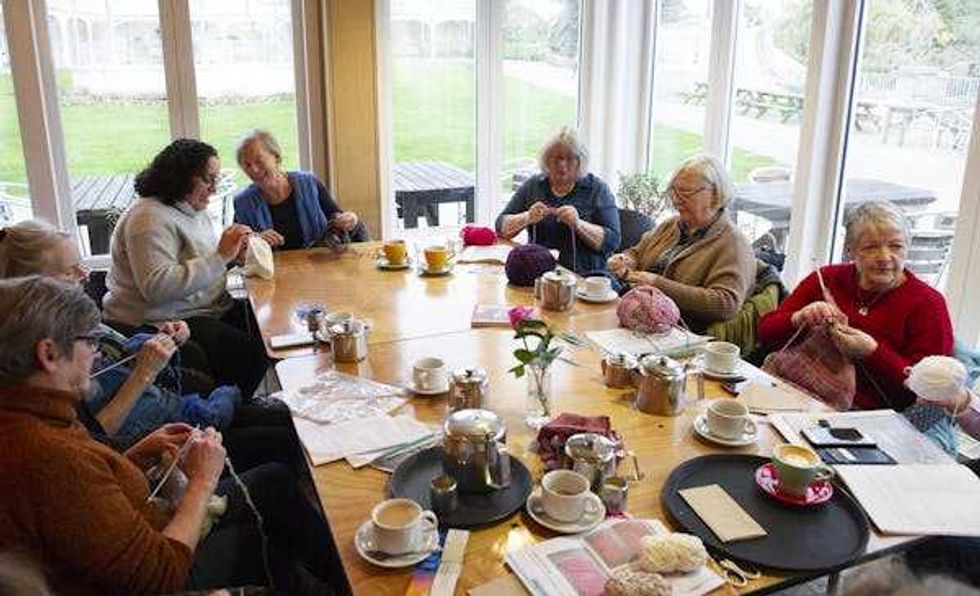 Tasks that stretch your brain just beyond its comfort zone, such as knitting and crocheting, can improve cognitive abilities over your lifespan – and doing them in a group setting brings an additional bonus for overall health.
Tasks that stretch your brain just beyond its comfort zone, such as knitting and crocheting, can improve cognitive abilities over your lifespan – and doing them in a group setting brings an additional bonus for overall health. Overdoing any task, whether it be weight training or sitting at the computer for too long, can overtax the muscles as well as the brain.
Overdoing any task, whether it be weight training or sitting at the computer for too long, can overtax the muscles as well as the brain.